Z288500
Aldrich® Imperial mini-spill kits
capacity 3.6 gal (13.6 L)
Autenticatiper visualizzare i prezzi riservati alla tua organizzazione & contrattuali
About This Item
Codice UNSPSC:
47131905
NACRES:
NB.35
Prodotti consigliati
Capacità
3.6 gal (13.6 L)
Cerchi prodotti simili? Visita Guida al confronto tra prodotti
Categorie correlate
Descrizione generale
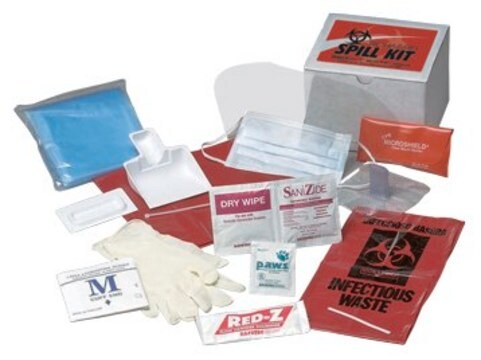
Designed for safely handling the cleanup of small chemical spills in the research laboratory. Kits feature "No Decision Response" universal polypropylene sorbent pads and "socks" that are suited for non-aggressive, hydrocarbon-based, and aggressive liquid leaks or spills.
Kit components are packed in a sturdy HDPE bucket with tight-fitting lid that is used for containment of used sorbents. Spill response instructions are printed on bucket label for fast access.
Caution: Care should be taken when using these sorbents to pick up fuming acids (such as nitric or sulfuric acid), as well as strong oxidizers since they may degrade the polypropylene material.
Kit components are packed in a sturdy HDPE bucket with tight-fitting lid that is used for containment of used sorbents. Spill response instructions are printed on bucket label for fast access.
Caution: Care should be taken when using these sorbents to pick up fuming acids (such as nitric or sulfuric acid), as well as strong oxidizers since they may degrade the polypropylene material.
Kit contents: ten 12×12 in. universal PP sorbent pads; two 3 in.×4 ft universal socks; one brush/pan kit; one pair nitrile gloves; one 18×30 in. disposal bag; one 5 gal HDPE bucket with lid.
Note legali
Aldrich is a registered trademark of Sigma-Aldrich Co. LLC
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Certificati d'analisi (COA)
Lot/Batch Number
It looks like we've run into a problem, but you can still download Certificates of Analysis from our Documenti section.
Se ti serve aiuto, non esitare a contattarci Servizio Clienti
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Giovanna Trinchese et al.
The Journal of nutritional biochemistry, 26(11), 1136-1146 (2015-06-30)
Different nutritional components are able, by modulating mitochondrial function and gut microbiota composition, to influence body composition, metabolic homeostasis and inflammatory state. In this study, we aimed to evaluate the effects produced by the supplementation of different milks on energy
Y Y Xiao et al.
Epidemiology and infection, 143(9), 1833-1838 (2014-11-02)
No published studies have discussed details of the prognosis and survival of patients with severe avian influenza A(H7N9) infection. In this study we analysed 128 laboratory-confirmed cases of severe H7N9 infection in Zhejiang province, the most affected region during the
Mark Zeller et al.
Molecular biology and evolution, 32(8), 2060-2071 (2015-04-11)
The majority of human group A rotaviruses possess the P[8] VP4 genotype. Recently, a genetically distinct subtype of the P[8] genotype, also known as OP354-like P[8] or lineage P[8]-4, emerged in several countries. However, it is unclear for how long
James Neil Fisher et al.
Oncotarget, 6(15), 13176-13200 (2015-05-12)
SKBR3-cells, characterized by ERBB2/RARA co-amplification, represent a subgroup of HER2+ breast-cancers sensitive to all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) and Lapatinib. In this model, the two agents alone or in combination modulate the expression of 174 microRNAs (miRs). These miRs and predicted
Monique Silvy et al.
Transfusion, 55(6 Pt 2), 1407-1410 (2014-11-22)
The rare amorph Rhnull phenotype is caused by silent alleles at the RH locus and usually arises in consanguineous families. To date, only five molecular backgrounds have been identified in five unrelated families. Subjects with Rhnull red blood cells (RBCs)
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.