906816
Water-soluble TPO based nanoparticle photoinitiator
contains nonionic surfactant
Sinonimo/i:
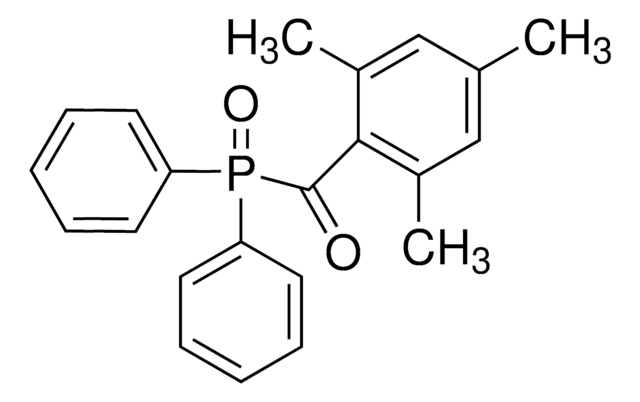
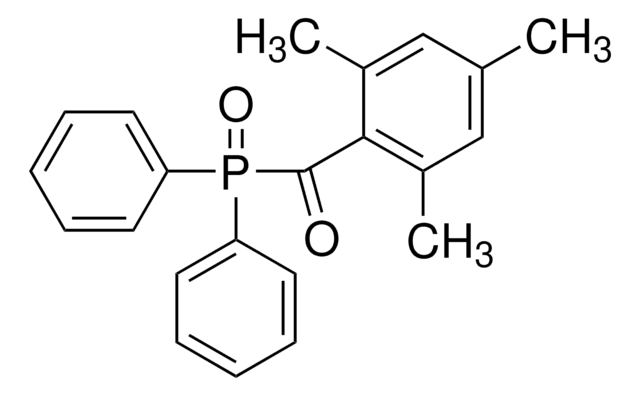
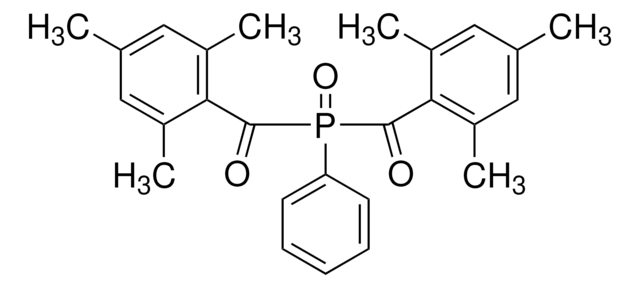
Diphenyl(2,4,6-trimethylbenzoyl)phosphine oxide, TPO
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Stato
powder or solid
Colore
white to off-white
Stringa SMILE
O=P(C1=CC=CC=C1)(C(C2=C(C)C=C(C)C=C2C)=O)C3=CC=CC=C3
Cerchi prodotti simili? Visita Guida al confronto tra prodotti
Applicazioni
The extinction coefficient of the new water-dispersible nanoparticles of TPO is more than 300 times larger than the best and most used commercially available water-soluble photoinitiator, Irgacure 2959. The TPO nanoparticles absorb significantly in the range from 385 to 420 nm, making them suitable for use in commercially available, low-cost, light-emitting diode-based 3D printers and UV-curing devices.
Avvertenze
Warning
Indicazioni di pericolo
Consigli di prudenza
Classi di pericolo
Aquatic Chronic 2 - Repr. 2 - Skin Sens. 1
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 3
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Certificati d'analisi (COA)
Non trovi la versione di tuo interesse?
Se hai bisogno di una versione specifica, puoi cercare il certificato tramite il numero di lotto.
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Articoli
The introduction of LAP and water-dispersible photoinitiator nanoparticles of TPO, enables the development of novel formulations for 3D bioprinting, tissue engineering applications, and device manufacturing.
Contenuto correlato
Tissue engineering fabricates tissues cultures from scaffolds, living cells, and biologically active molecules by simulating the microenvironment of the body to repair or replace damaged tissue.
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.