765147
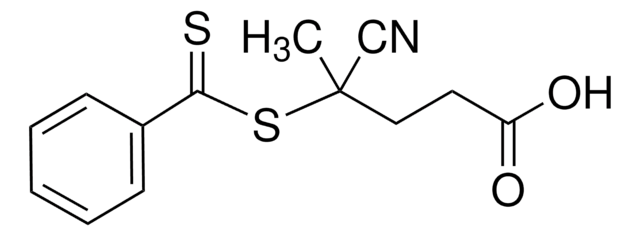
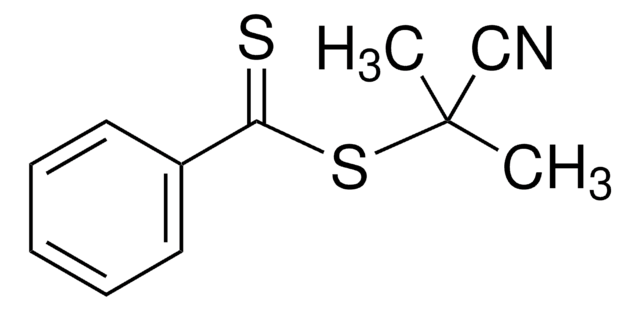
2-Nitro-5-(2-propynyloxy)benzyl 4-cyano-4-(phenylcarbonothioylthio)pentanoate
97%
Sinonimo/i:
Clickable CTA, Light-sensitive clickable RAFT agent, RAFT agent
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Saggio
97%
Forma fisica
solid
Punto di fusione
90-94 °C
Temperatura di conservazione
2-8°C
Stringa SMILE
C#CCOC1=CC(COC(CCC(C)(C#N)SC(C2=CC=CC=C2)=S)=O)=C([N+]([O-])=O)C=C1
InChI
1S/C23H20N2O5S2/c1-3-13-29-19-9-10-20(25(27)28)18(14-19)15-30-21(26)11-12-23(2,16-24)32-22(31)17-7-5-4-6-8-17/h1,4-10,14H,11-13,15H2,2H3
IOYDTDXAMFFKOA-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Descrizione generale
Applicazioni
Avvertenze
Warning
Indicazioni di pericolo
Consigli di prudenza
Classi di pericolo
Aquatic Acute 1 - Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Sens. 1
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Certificati d'analisi (COA)
Non trovi la versione di tuo interesse?
Se hai bisogno di una versione specifica, puoi cercare il certificato tramite il numero di lotto.
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Articoli
The modification of biomacromolecules, such as peptides and proteins, through the attachment of synthetic polymers has led to a new family of highly advanced biomaterials with enhanced properties.
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.![Pentaerythritol tetrakis[2-(dodecylthiocarbonothioylthio)-2-methylpropionate] 97% (HPLC)](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/234/301/a6e20d26-df1b-49c6-bdee-c98dd3488cc2/640/a6e20d26-df1b-49c6-bdee-c98dd3488cc2.png)