731129
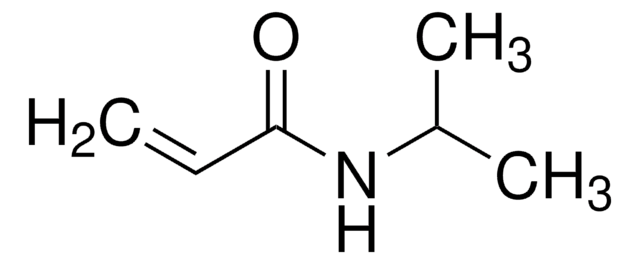
N-Isopropylacrylamide
≥99%
Sinonimo/i:
NIPAM
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Livello qualitativo
Saggio
≥99%
Forma fisica
flakes
P. eboll.
89-92 °C/2 mmHg (lit.)
Punto di fusione
60-63 °C (lit.)
63-67 °C
Temperatura di conservazione
2-8°C
Stringa SMILE
CC(C)NC(=O)C=C
InChI
1S/C6H11NO/c1-4-6(8)7-5(2)3/h4-5H,1H2,2-3H3,(H,7,8)
QNILTEGFHQSKFF-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Cerchi prodotti simili? Visita Guida al confronto tra prodotti
Descrizione generale
Applicazioni
N-Isopropylacrylamide can also be used as a key component in:
- The synthesis of self-powered multifunctional organic hydrogel based on poly(acrylic acid-N-isopropyl acrylamide) for flexible sensing devices.
- The development of a new type of flexible and stable gel electrolyte for aqueous Zn-MnO2 batteries.
- The preparation of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide/itaconic acid) (PNIPAM/IA) copolymeric hydrogels for drug delivery applications.
- The synthesis of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAM) polymer for the development of a new class of polymer-grafted semiconductor devices.
Avvertenze
Danger
Indicazioni di pericolo
Consigli di prudenza
Classi di pericolo
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Eye Dam. 1
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 3
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Articoli
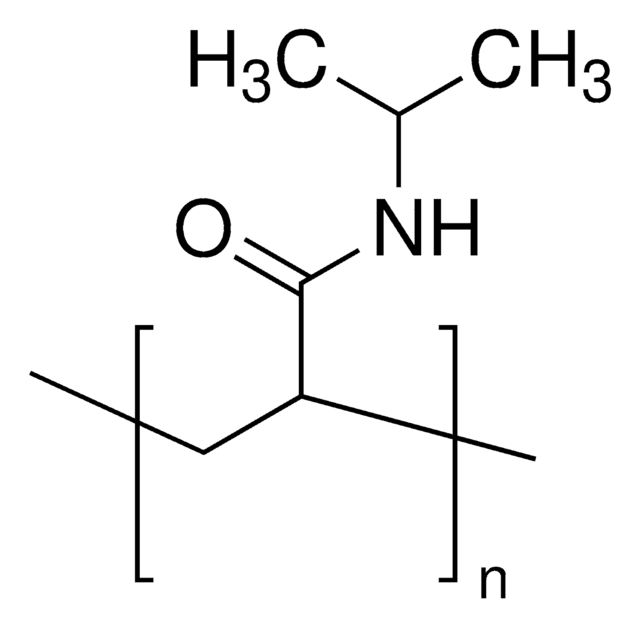
Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide), or PNIPAM, is a stimuli-responsive polymer that responds to changes in pH and temperature and has a LCST around 32 C.
Tissue engineering has become a key therapeutic tool in the treatment of damaged or diseased organs and tissues, such as blood vessels and urinary bladders.
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.