430471
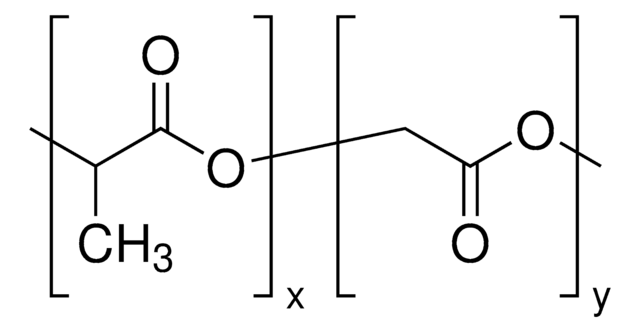
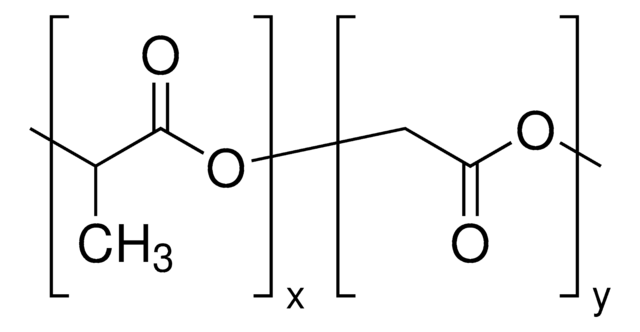
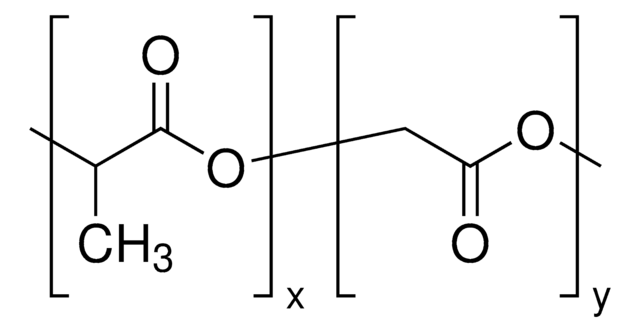
Poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide)
ester terminated, Mw 50,000-75,000
Sinonimo/i:
Lactel® B6006-1, PLGA
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Livello qualitativo
Stato
amorphous
Rapporto d’alimentazione
lactide:glycolide 85:15
PM
Mw 50,000-75,000
Tempo di degradazione
<6 months
Viscosità
0.55-0.75 dL/g, 0.1 % (w/v) in chloroform(25 °C)
Temp. transizione
Tg 45-50 °C
Solubilità
ethyl acetate, chloroform, acetone and THF: soluble
Temperatura di conservazione
2-8°C
Stringa SMILE
OCC(O)=O.CC(O)C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C3H6O3.C2H4O3/c1-2(4)3(5)6;3-1-2(4)5/h2,4H,1H3,(H,5,6);3H,1H2,(H,4,5)
XBBVURRQGJPTHH-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Cerchi prodotti simili? Visita Guida al confronto tra prodotti
Categorie correlate
Descrizione generale
Applicazioni
Caratteristiche e vantaggi
Stato fisico
Note legali
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Dispositivi di protezione individuale
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Articoli
The world of commercial biomaterials has stagnated over the past 30 years as few materials have successfully transitioned from the bench to clinical use. Synthetic aliphatic polyesters have continued to dominate the field of resorbable biomaterials due to their long history and track record of approval with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
Aliphatic polyesters such as polylactide, poly(lactide-co-glycolide) and polycaprolactone, as well as their copolymers, represent a diverse family of synthetic biodegradable polymers that have been widely explored for medical uses and are commercially available.
Aliphatic polyesters such as polylactide, poly(lactide-co-glycolide) and polycaprolactone, as well as their copolymers, represent a diverse family of synthetic biodegradable polymers that have been widely explored for medical uses and are commercially available.
In the past two decades, tissue engineering and regenerative medicine have become important interdisciplinary fields that span biology, chemistry, engineering, and medicine.
Contenuto correlato
Interest in utilizing biodegradable polymers for biomedical applications has grown since the 1960s.
Global Trade Item Number
| SKU | GTIN |
|---|---|
| 430471-1G | 4061835563029 |
| 430471-5G | 4061835563036 |
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.