A7653
L-Alanine Dehydrogenase from Bacillus subtilis
buffered aqueous glycerol solution, ~30 units/mg protein (Lowry)
Synonym(s):
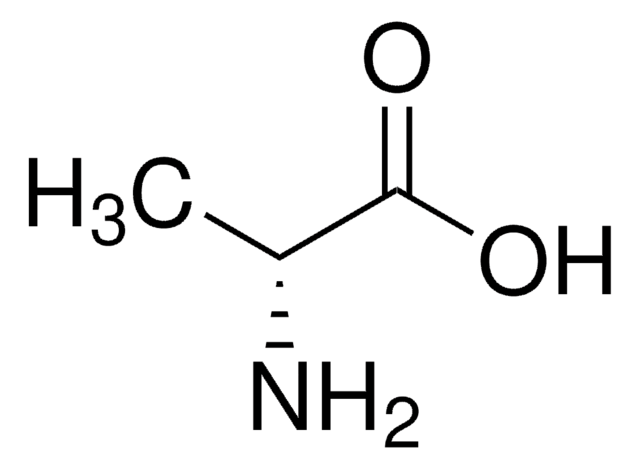
L-Alanine: NAD+ oxidoreductase (deaminating)
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
Bacillus subtilis
Quality Level
form
buffered aqueous glycerol solution
specific activity
~30 units/mg protein (Lowry)
foreign activity
LDH ~1% (using pyruvate as substrate)
storage temp.
−20°C
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Application
L-Alanine dehydrogenase converts L-alanine to pyruvate and ammonium. L-Alanine dehydrogenase from Bacillus subtilis may be used to study enzyme inactivation and protection .
Biochem/physiol Actions
L-Alanine dehydrogenase is an A-stereospecific dehydrogenase that catalyzes the reversible deamination of L-alanine to pyruvate and ammonium. It is important for the generation of pyruvate during sporulation. L-Alanine dehydrogenase from Bacillus subtilis has a predominately ordered kinetic mechanism in which NAD binds before L-alanine. Subsequently, ammonia, pyruvate, and NADH are released in that specific order. Optimal pH for the amination reaction is 8.8-9.0, whereas it is 10-10.5 for the deamination reaction. The enzyme is inactivated by divalent metal ions and p-chloromercuribenzoate, mercuric ion being most effective. The inactivation may be reversed by L- or D-cysteine.
Unit Definition
One unit will convert 1.0 μmole of L-alanine to pyruvate and NH3 per min at pH 10.0 at 25 °C.
Physical form
Solution in 50% glycerol containing 10 mM potassium phosphate buffer, pH 7.7
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Resp. Sens. 1
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 3
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
D Delforge et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 272(4), 2276-2284 (1997-01-24)
L-Alanine dehydrogenase from Bacillus subtilis was inactivated with two different lysine-directed chemical reagents, i.e. 2,4, 6-trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid and N-succinimidyl 3-(2-pyridyldithio)propionate. In both cases, the inactivation followed pseudo first-order kinetics, with a 1:1 stoichiometric ratio between the reagent and the enzyme
Hexigeduleng Bao et al.
Plant, cell & environment, 38(3), 600-613 (2014-07-31)
γ-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) accumulates in many plant species in response to environmental stress. However, the physiological function of GABA or its metabolic pathway (GABA shunt) in plants remains largely unclear. Here, the genes, including glutamate decarboxylases (SlGADs), GABA transaminases (SlGABA-Ts) and
Xueli Zhang et al.
Applied microbiology and biotechnology, 77(2), 355-366 (2007-09-18)
Escherichia coli W was genetically engineered to produce L: -alanine as the primary fermentation product from sugars by replacing the native D: -lactate dehydrogenase of E. coli SZ194 with alanine dehydrogenase from Geobacillus stearothermophilus. As a result, the heterologous alanine
Toru Jojima et al.
Applied microbiology and biotechnology, 87(1), 159-165 (2010-03-11)
Corynebacterium glutamicum was genetically engineered to produce L-alanine from sugar under oxygen deprivation. The genes associated with production of organic acids in C. glutamicum were inactivated and the alanine dehydrogenase gene (alaD) from Lysinibacillus sphaericus was overexpressed to direct carbon
Senay Hamarat Baysal et al.
Artificial cells, blood substitutes, and immobilization biotechnology, 35(4), 391-403 (2007-08-19)
Urease and AlaDH enzymes immobilized on active PEG derivatives were encapsulated at different ratios within sheep erythrocytes and their activity, encapsulation yields and erythrocyte recovery levels were assessed. Encapsulated derivatives were administered at given dosages and at given intervals to
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service