推荐产品
品質等級
化驗
≥98% (HPLC)
形狀
powder
顏色
white to beige
溶解度
DMSO: 2 mg/mL, clear
儲存溫度
2-8°C
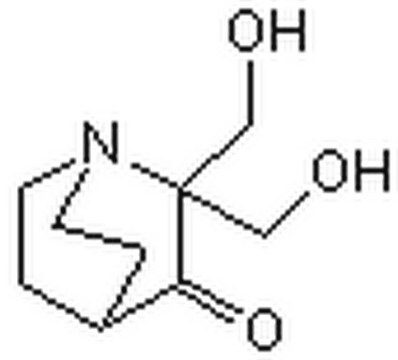
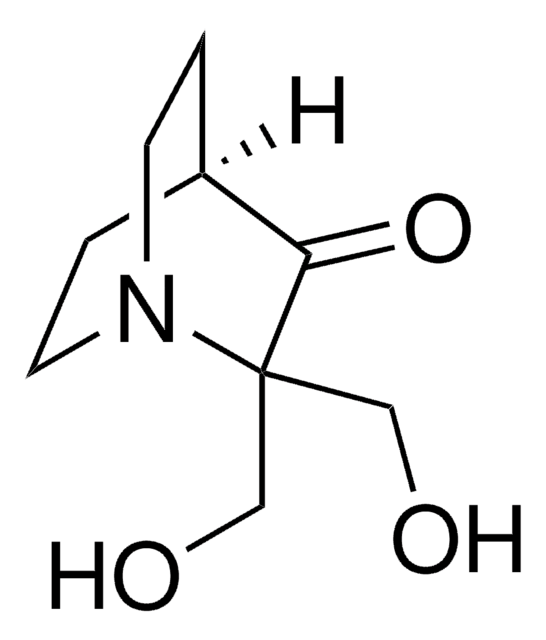
InChI
1S/C10H17NO3/c1-14-7-10(6-12)9(13)8-2-4-11(10)5-3-8/h8,12H,2-7H2,1H3
InChI 密鑰
BGBNULCRKBVAKL-UHFFFAOYSA-N
生化/生理作用
PRIMA-1Met (APR-246) is a re-activator of mutant p53 activity. It′s the methylated, more potent derivative of PRIMA-1. PRIMA-1Met covalently modifies the core domain of mutated p53 restoring the wild-type conformation and activty of p53 in tumor cells, leading to cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. PRIMA-1Met has also been shown to increase intracellular levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which may contribute to its anti-tumor activity.
PRIMA-1Met, also called APR-246, is converted to methylene quinuclidinone (MQ), a Michael acceptor. It interacts with p53 through the cysteine (Cys) residue. It blocks the thioredoxin reductase (TrxR1) enzyme. It is under clinical investigation and well-studied. PRIMA-1Met effect is tested on breast cancer specific gene expression.
訊號詞
Warning
危險聲明
危險分類
Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2
儲存類別代碼
11 - Combustible Solids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 3
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
APR-246/PRIMA-1 MET inhibits thioredoxin reductase 1 and converts the enzyme to a dedicated NADPH oxidase
Peng X, et al.
Cell Death & Disease, 4(10), e881-e881 (2013)
Christophe Deben et al.
Cancer letters, 375(2), 313-322 (2016-03-16)
APR-246 (PRIMA-1(Met)) is able to bind mutant p53 and restore its normal conformation and function. The compound has also been shown to increase intracellular ROS levels. Importantly, the poly-[ADP-ribose] polymerase-1 (PARP-1) enzyme plays an important role in the repair of
The mutant p53-targeting compound APR-246 induces ROS-modulating genes in breast cancer cells
Synnott N, et al.
Translational Oncology, 11(6) (2018)
Nobuhisa Yoshikawa et al.
Oncology reports, 35(5), 2543-2552 (2016-03-18)
There is an intensive need for the development of novel drugs for the treatment of epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC), the most lethal gynecologic malignancy due to the high recurrence rate. TP53 mutation is a common event in EOC, particularly in
Vladimir J N Bykov et al.
Frontiers in oncology, 6, 21-21 (2016-02-13)
TP53 is the most frequently mutated gene in cancer. The p53 protein activates transcription of genes that promote cell cycle arrest or apoptosis, or regulate cell metabolism, and other processes. Missense mutations in TP53 abolish specific DNA binding of p53
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门