推荐产品
品質等級
化驗
≥98% (HPLC)
形狀
powder
顏色
white to beige
溶解度
DMSO: 5 mg/mL, clear (warmed)
儲存溫度
2-8°C
SMILES 字串
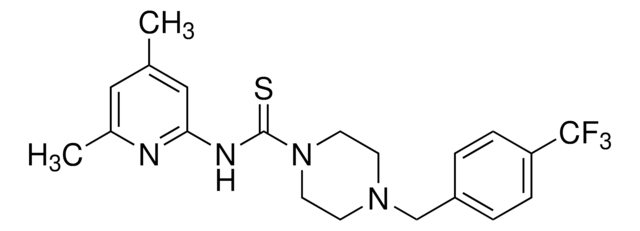
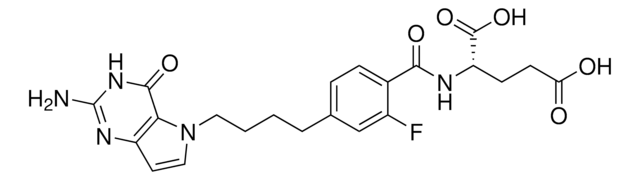
CC1=CC(NC(N2CCN(C3=CC=NC=C3)CC2)=S)=NC(C)=C1
InChI
1S/C17H21N5S/c1-13-11-14(2)19-16(12-13)20-17(23)22-9-7-21(8-10-22)15-3-5-18-6-4-15/h3-6,11-12H,7-10H2,1-2H3,(H,19,20,23)
InChI 密鑰
ITLPIAAGIQAGRA-UHFFFAOYSA-N
應用
NCT-503 Inactive Control has been used as a small molecule inhibitor of phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase in neuroblastoma cells.
生化/生理作用
NCT-503 Inactive Control is the inactive control probe for NCT-503, which is an inhibitor of phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase (PHGDH), the enzyme that catalyzes the first, rate-limiting step of glucose-derived serine synthesis. NCT-503 Inactive Control has an IC50 value >57 μM for PHGDH. NCT-503 has an IC50 value of 2.5 μM for PHGDH. NCT-503 Inactive Control is water soluble and has good stability, similar to NCT-503.
推薦產品
The active PHGDH inhibitor, NCT-503, is available from Sigma. To learn more about and purchase NCT-503, click here.
訊號詞
Warning
危險聲明
危險分類
Skin Irrit. 2
儲存類別代碼
11 - Combustible Solids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 3
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
Birte Arlt et al.
Journal of enzyme inhibition and medicinal chemistry, 36(1), 1282-1289 (2021-07-02)
The small-molecule inhibitor of phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase, NCT-503, reduces incorporation of glucose-derived carbons into serine in vitro. Here we describe an off-target effect of NCT-503 in neuroblastoma cell lines expressing divergent phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase (PHGDH) levels and single-cell clones with CRISPR-Cas9-directed PHGDH
Yingfeng Xia et al.
Cancer research, 79(15), 3837-3850 (2019-05-16)
MYCN amplification drives the development of neuronal cancers in children and adults. Given the challenge in therapeutically targeting MYCN directly, we searched for MYCN-activated metabolic pathways as potential drug targets. Here we report that neuroblastoma cells with MYCN amplification show
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门