推荐产品
生物源
rabbit
品質等級
抗體表格
IgG fraction of antiserum
抗體產品種類
primary antibodies
形狀
liquid
物種活性
(Akkermancia muciniphila)
包裝
pkg of 100 μL
pkg of 25 μL
濃度
~1 mg/mL
技術
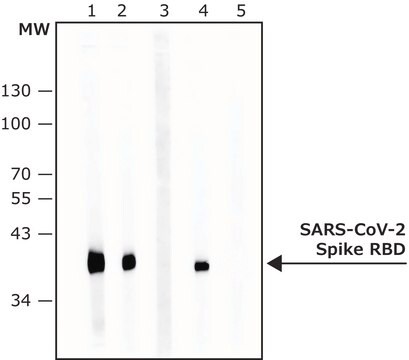
immunoblotting: 1:500-1:1000 using Akkermansia muciniphila lysate
運輸包裝
dry ice
儲存溫度
−20°C
目標翻譯後修改
unmodified
一般說明
Akkermansia muciniphila is a Gram negative, oval shaped, non-motile, non-spore forming strictly anaerobic bacteria.1 A. muciniphila colonized in the mucus layer of the human intestine niche. A muciniphila inhabits the gastrointestinal tracts of most of healthy adults and represents 1-4% of the total fecal microbiota starting from early life.2 It is one of the top 20 most abundant species detectable in the human gut.3 It was found that A. muciniphila abundance in the gut was correlated to a healthy intestine and inversely correlated to many disease conditions.2 In comparison to healthy controls, A. muciniphila levels were low in intestinal disorders, such inflammatory bowel disease IBD, but also in other conditions, such as autism, atopy, and obesity.2,5-8 Therefore, A. muciniphila was suggested to serve as a marker of healthy intestine.
In addition, goring research identified A. muciniphila as a promising potential probiotic that can be administrated for the treatment of diseases such as, colitis, metabolic syndromes, immune diseases and cancer. However more research is needed to verify the safety of oral administration of A. muciniphila in humans.3
In addition, goring research identified A. muciniphila as a promising potential probiotic that can be administrated for the treatment of diseases such as, colitis, metabolic syndromes, immune diseases and cancer. However more research is needed to verify the safety of oral administration of A. muciniphila in humans.3
特異性
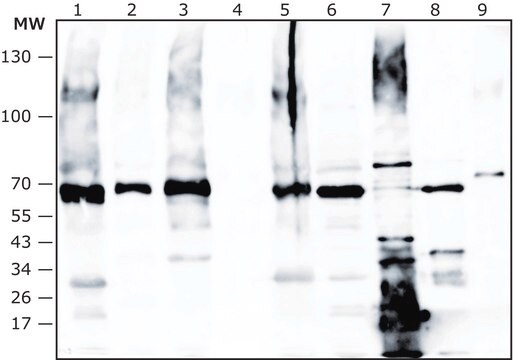
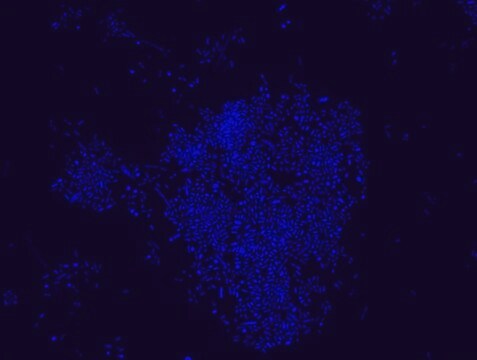
Anti-Akkermansia muciniphila antibody recognizes A. muciniphila lysate and whole dead bacteria.
生化/生理作用
A. muciniphila is able to degrade mucin, a key mucus component, using the enzymes sialidase and fucosidase, and utilize it as a source of carbon and nitrogen.2 Mucin degradation by A. muciniphila results in the production of short-chain fatty acids (SCFA), that become available metabolites to the host and also can stimulate the host immune system. Moreover, SCFA promotes the growth and metabolic activity of mucus- associated gut microbiota preventing the pathogenic bacteria from reaching the intestinal cells.4
外觀
Supplied as a solution in 0.01 M phosphate buffered saline pH 7.4, containing 15 mM sodium azide as a preservative.
儲存和穩定性
For continuous use, store at 2-8°C for up to one month. For extended storage, freeze in working aliquots. Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. If slight turbidity occurs upon prolonged storage, clarify the solution by centrifugation before use. Working dilution samples should be discarded if not used within 12 hours.
免責聲明
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
未找到合适的产品?
试试我们的产品选型工具.
儲存類別代碼
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
nwg
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
Ting Zhang et al.
Microbial biotechnology, 12(6), 1109-1125 (2019-04-23)
Akkermansia muciniphila (A. muciniphila), an intestinal symbiont colonizing in the mucosal layer, is considered to be a promising candidate as probiotics. A. muciniphila is known to have an important value in improving the host metabolic functions and immune responses. Moreover, A. muciniphila may
A Santacruz et al.
The British journal of nutrition, 104(1), 83-92 (2010-03-09)
Obesity is associated with complications during pregnancy and increased health risks in the newborn. The objective of the present study was to establish possible relationships between gut microbiota, body weight, weight gain and biochemical parameters in pregnant women. Fifty pregnant
Muriel Derrien et al.
International journal of systematic and evolutionary microbiology, 54(Pt 5), 1469-1476 (2004-09-25)
The diversity of mucin-degrading bacteria in the human intestine was investigated by combining culture and 16S rRNA-dependent approaches. A dominant bacterium, strain MucT, was isolated by dilution to extinction of faeces in anaerobic medium containing gastric mucin as the sole
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门