SAB4200625
Anti-Methyl-Histone H3 (Me-Lys9)(H3K9me1) antibody, Mouse monoclonal
clone 7E7-H12, purified from hybridoma cell culture
别名:
9430068D06RIK, H3.3A, H3.3B, H3F3, H3F3A, H3F3A/H3F3B, H3F3B, HISTONE 3B, LOC100045490, RP11−396C23.1, wu:fb58e10, zgc:56193, zgc:86731
登录查看公司和协议定价
所有图片(2)
About This Item
分類程式碼代碼:
12352203
NACRES:
NA.41
推荐产品
生物源
mouse
品質等級
共軛
unconjugated
抗體表格
purified immunoglobulin
抗體產品種類
primary antibodies
無性繁殖
7E7-H12, monoclonal
形狀
buffered aqueous solution
分子量
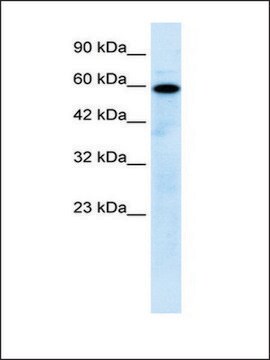
antigen ~17 kDa
物種活性
human
濃度
~1 mg/mL
技術
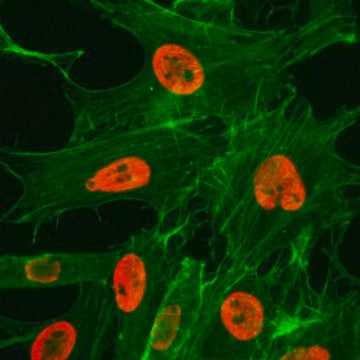
immunoblotting: 2.5-5 μg/mL using human HeLa cells.
immunocytochemistry: 2.5-5 μg/mL using human HeLa cells.
同型
IgG1
運輸包裝
dry ice
儲存溫度
−20°C
目標翻譯後修改
monomethylation (Lys9)
基因資訊
human ... H3C1(8350)
一般說明
Anti-Methyl-Histone H3 (Me-Lys9) (H3K9me1) antibody, Mouse Monoclonal (mouse IgG1 isotype) is derived from the hybridoma 7E7-H12 produced by the fusion of mouse myeloma cells and splenocytes from BALB/c mice immunized with a methylated (Me-Lys9) peptide corresponding to the N-terminus of human histone H3, conjugated to KLH.
免疫原
Methylated (Me-Lys9) peptide corresponding to the N-terminus of human histone H3, conjugated to KLH.
應用
Anti-Methyl-Histone H3 (Me-Lys9) (H3K9me1) antibody has been used in immunoblotting and immunocytochemistry.
生化/生理作用
Histones are subjected to extensive covalent modifications that play an important role in development and in cancer. These modifications include phosphorylation, methylation, acetylation and ubiquitination. Histones H3 and H4 are the predominant histones modified by methylation and are highly methylated in mammalian cells. Histone methylation, like acetylation, is a complex, dynamic process involving several processes, including transcriptional regulation, chromatin condensation, mitosis, and heterochromatin assembly. Moreover, lysine residues can be mono-, di-, and tri-methylated, adding further complexity to the regulation of chromatin structure. Conserved lysine residues in the N-terminal tail domains of histone H3, Lys4, Lys9 and Lys27 are the preferred sites of methylation. Methylation of H3 at Lys9 is a modification intrinsically linked to epigenetic silencing and heterochromatin assembly.
外觀
Solution in 0.01 M phosphate buffered saline, pH 7.4, containing 15 mM sodium azide.
免責聲明
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
未找到合适的产品?
试试我们的产品选型工具.
儲存類別代碼
10 - Combustible liquids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 1
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
Methylation of histone H3 at lysine 4 is highly conserved and correlates with transcriptionally active nuclei in Tetrahymena
Strahl B D, et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA, 96(26), 14967-14972 (1999)
Cancer epigenetics: from mechanism to therapy
Dawson M A and Kouzarides T
Cell, 150(1), 12-27 (2012)
B D Strahl et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 96(26), 14967-14972 (1999-12-28)
Studies into posttranslational modifications of histones, notably acetylation, have yielded important insights into the dynamic nature of chromatin structure and its fundamental role in gene expression. The roles of other covalent histone modifications remain poorly understood. To gain further insight
Mark A Dawson et al.
Cell, 150(1), 12-27 (2012-07-10)
The epigenetic regulation of DNA-templated processes has been intensely studied over the last 15 years. DNA methylation, histone modification, nucleosome remodeling, and RNA-mediated targeting regulate many biological processes that are fundamental to the genesis of cancer. Here, we present the
Tony Kouzarides
Cell, 128(4), 693-705 (2007-02-27)
The surface of nucleosomes is studded with a multiplicity of modifications. At least eight different classes have been characterized to date and many different sites have been identified for each class. Operationally, modifications function either by disrupting chromatin contacts or
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门