推荐产品
應用
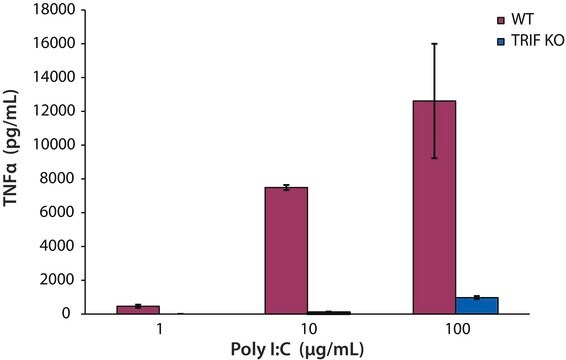
TLR3可识别双链RNA,是病毒病原体免疫应答的主要效应物。 聚肌苷酸-聚胞苷酸 (Poly(I) • Poly(C))是一种双链均聚物,可作为模型RNA,用于研究在TLR3水平下的细胞信号传导。 Poly(IC)是TRIF依赖型toll样受体3(TLR3)的配体。
生化/生理作用
将Poly(I:C)转染至NIT-1细胞中,已被用作细胞内dsRNA诱导的β细胞凋亡的模型。转染后18小时,45%的细胞发生凋亡,并且其NF-kB、p50/p65核转位、caspase 3和8切割以及caspase 12的转录诱导、Fas、IL-15和TNF受体相关配体(TRAIL)水平均增加。有人提出Poly(I:C)是最合适的稳定成熟树突状细胞(DC)诱导剂之一。这些成熟DC能够在CD40连接后分泌生物活性IL-12,因此注射后能够在体内产生有效的免疫应答。Poly(I:C)被用作有效的佐剂,以增强对肽类疫苗的特异性抗肿瘤免疫应答。
包裝
包装规格取决于多核苷酸含量
其他說明
双链均聚物。
準備報告
本品需要离子强度,以维持双链结构。用水复溶至浓度约为10 mg/mL,获得溶于生理磷酸盐缓冲溶液的多核苷酸。
儲存類別代碼
11 - Combustible Solids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 3
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
個人防護裝備
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
其他客户在看
Marie Anaïs Labouesse et al.
Epigenetics, 10(12), 1143-1155 (2015-11-18)
Maternal infection during pregnancy increases the risk of neurodevelopmental disorders in the offspring. In addition to its influence on other neuronal systems, this early-life environmental adversity has been shown to negatively affect cortical γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) functions in adult life
Wei-Li Wu et al.
Brain, behavior, and immunity, 62, 11-23 (2016-11-14)
Epidemiological studies show that maternal immune activation (MIA) during pregnancy is a risk factor for autism. However, mechanisms for how MIA affects brain development and behaviors in offspring remain poorly described. To determine whether placental interleukin-6 (IL-6) signaling is required
Jun-Sang Sunwoo et al.
Annals of clinical and translational neurology, 5(10), 1264-1276 (2018-10-24)
Maternal immune activation (MIA) is associated with an increased risk of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) in offspring. Herein, we investigate the altered expression of microRNAs (miRNA), and that of their target genes, in the brains of MIA mouse offspring. To
Halime Kalkavan et al.
Nature communications, 8, 14447-14447 (2017-03-02)
Immune-mediated effector molecules can limit cancer growth, but lack of sustained immune activation in the tumour microenvironment restricts antitumour immunity. New therapeutic approaches that induce a strong and prolonged immune activation would represent a major immunotherapeutic advance. Here we show
William R Crum et al.
Brain, behavior, and immunity, 63, 50-59 (2016-12-13)
Genetic and environmental risk factors for psychiatric disorders are suggested to disrupt the trajectory of brain maturation during adolescence, leading to the development of psychopathology in adulthood. Rodent models are powerful tools to dissect the specific effects of such risk
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门