推荐产品
生物源
mouse
品質等級
共軛
unconjugated
抗體表格
ascites fluid
抗體產品種類
primary antibodies
無性繁殖
LEP-13, monoclonal
分子量
antigen 16 kDa
包含
15 mM sodium azide
物種活性
human
技術
indirect ELISA: suitable
radioimmunoassay: suitable
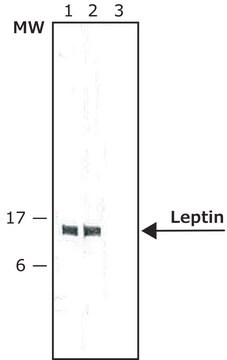
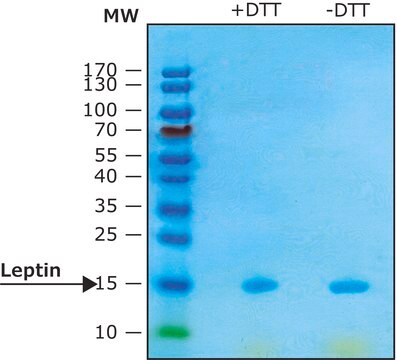
western blot: 1:1,000 using recombinant human leptin
同型
IgG1
UniProt登錄號
運輸包裝
dry ice
儲存溫度
−20°C
目標翻譯後修改
unmodified
SMILES 字串
ClC(Cl)(Cl)C(c2c(c(c(c(c2[2H])[2H])Cl)[2H])[2H])c1c(c(c(c(c1[2H])[2H])Cl)[2H])[2H]
InChI
1S/C14H9Cl5/c15-11-5-1-9(2-6-11)13(14(17,18)19)10-3-7-12(16)8-4-10/h1-8,13H/i1D,2D,3D,4D,5D,6D,7D,8D
InChI 密鑰
YVGGHNCTFXOJCH-PGRXLJNUSA-N
基因資訊
human ... LEP(3952)
一般說明
Leptin is a hormone secreted by adipocytes and regulates energy homeostasis, inflammation and neuroendocrine processes, synaptic formation and memory condensation. The physiological effects of leptin are mediated by leptin receptors, ObR and LepR. The receptors are present in brain, lungs, kidneys, liver and adipose tissue. Leptin is the key regulator of obesity and acts directly on neuronal networks to regulate feeding, metabolism, gastric mobility and energy homeostasis. The pathways that mediate the effect of leptin are JAK/STAT, PI3K and JNK. Deficiency of leptin may be a congenital condition and results in thyroid axis abnormalities.. Monoclonal Anti-Leptin reacts specifically with human leptin. A weak cross reactivity with mouse leptin is observed in radioimmunoassay.
Monoclonal Anti-Leptin (OB) (mouse IgG isotype) is derived from the LEP-13 hybridoma produced by the fusion of mouse myeloma cells and splenocytes from BALB/c mice immunized with a recombinant human leptin. Leptin (also known as OB, the product of the ob gene) is a 16 kDa, 146 amino acid residue, non-glycosylated polypeptide, secreted by the mature adipocyte. It is strongly expressed in white adipose tissue, and is absent or expressed at extremely low levels in other tissues. The human leptin molecule is translated as a 167 amino acid residue polypeptide, with the first 21 amino acid residues cleaved as a signal peptide.
特異性
The antibody reacts specifically with human leptin. By RIA, weak cross-reactivity has been observed with recombinant mouse leptin.
免疫原
recombinant human leptin.
應用
Monoclonal Anti-Leptin antibody produced in mouse has been used in western blotting. It may be used in radioimmunoassay (RIA) and enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
生化/生理作用
Leptin is hypothesized to be a ′′satiety factor′′, because the absence of this factor was associated with hyperphagia and obesity. Leptin is involved in appetite regulation. Human obesity is often associated with increased blood leptin levels. Leptin acts through discrete receptors and distant targets to create a feedback loop for body weight regulation. With respect to the target of leptin action, the hypothalamus has received a great deal of attention. The leptin system has also been proposed to contribute to early hematopoiesis.
免責聲明
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
未找到合适的产品?
试试我们的产品选型工具.
儲存類別代碼
10 - Combustible liquids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 3
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
Anna Ptak et al.
Toxicology letters, 210(3), 332-337 (2012-02-22)
We previously demonstrated that bisphenol A (BPA) promotes proliferation in OVCAR-3 human ovarian cancer cells. This study was designed to investigate the effects of BPA on leptin expression and activity in ovarian cancer. Real-time PCR, Western blot analysis and ELISA
Superactive human leptin antagonist reverses leptin-induced excessive progesterone and testosterone secretion in porcine ovarian follicles by blocking leptin receptors
Gregoraszczuk EL and Rak A
Journal of Physiology And Pharmacology, 66(3), 39-46 (2015)
Narrative review: the role of leptin in human physiology: emerging clinical applications
Kelesidis T, et al.
Annals of Internal Medicine, 152(2), 93-93 (2010)
Bisphenol A induces leptin receptor expression, creating more binding sites for leptin, and activates the JAK/Stat, MAPK/ERK and PI3K/Akt signalling pathways in human ovarian cancer cell
Ptak A and Gregoraszczuk EL
Toxicology Letters, 210(3), 332-337 (2012)
Weihong Pan et al.
Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1264, 64-71 (2012-04-26)
Leptin, an adipocyte-derived cytokine, crosses the blood-brain barrier to act on many regions of the central nervous system (CNS). It participates in the regulation of energy balance, inflammatory processes, immune regulation, synaptic formation, memory condensation, and neurotrophic activities. This review
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门