推荐产品
生物源
rabbit
共軛
unconjugated
抗體表格
affinity isolated antibody
抗體產品種類
primary antibodies
無性繁殖
polyclonal
形狀
buffered aqueous solution
分子量
antigen 70 kDa
物種活性
rat, mouse, human, bovine
加強驗證
independent
Learn more about Antibody Enhanced Validation
技術
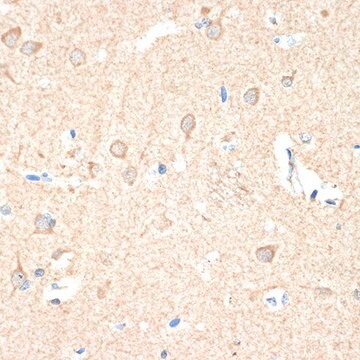
immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded sections): 1:400 using trypsin-digested human, bovine and mouse heart tissue
immunoprecipitation (IP): 2-3 μg using 60-120 μg of a cytosolic fraction of rat brain
western blot: 1:2,000 using cytosolic fraction of rat brain
運輸包裝
dry ice
儲存溫度
−20°C
目標翻譯後修改
unmodified
基因資訊
human ... GUCY1B3(2983)
mouse ... Gucy1b3(54195)
rat ... Gucy1b3(25202)
一般說明
Soluble guanylyl cyclase (sGC) is an obligate hemoprotein enzyme consisting of α and β subunits of ~80 kDa and ~70 kDa, respectively.
免疫原
synthetic peptide corresponding to amino acid residues 189-207, with N-terminal added lysine, of rat soluble guanylate cyclase 1, conjugated to KLH with glutaraldehyde. The sequence differs in human, bovine and mouse by 1 amino acid.
應用
Anti-Guanylyl Cyclase β1 (ER-19) antibody produced in rabbit is suitable for immunoblotting at a working dilution of 1:2000 using a cytosolic fraction of rat brain, immunoprecipitation at a working antibody amount of 2-3μg using 60-120μg of a cytosolic fraction of rat brain and for immunohistochemistry at 1:400 using trypsin-digested human, bovine and mouse heart tissue.
It has been used as a primary antibody for:
It has been used as a primary antibody for:
- localization of β1 subunits of sGC (soluble guanylate cyclase) in the guinea pig gastrointestinal tract
- detection of expression of sGC in the vasculature of rat skeletal muscle
- localization of the functional subunit of NO receptors, sGCβ1 in guinea pig caecum
生化/生理作用
Guanylyl cyclase (GC) catalyzes the conversion of guanosine-5′–triphosphate (GTP) to cyclic guanosine-3′,5-monophosphate (cGMP) and pyrophosphate. This reaction requires Mg2+ or Mn2+. Both the units are required for catalytic activity. The N-terminal domains of the subunits are essential for the stimulation of the enzyme by NO. Dimerization is mediated by the central portion of GC. The C-terminus domain of both subunits forms the catalytic domain.
The enzyme (GC) is a major physiological receptor for nitric oxide (NO), an important intra- and intercellular membrane-permeant signaling molecule. Gaseous NO binds to Fe2+ in the prosthetic heme group of the enzyme. NO binding is followed by disruption of the β1 subunit histidine105 bond to iron and activation of the enzyme. GC forms a complex with NO and cGMP and regulates smooth muscle relaxation, inflammation, platelet adhesion and aggregation, pulmonary physiology and neuronal function. It is an important target for NO-releasing and non-NO-releasing activator drugs in human cardiovascular therapy.
外觀
Solution in 0.01 M phosphate buffered saline, pH 7.4, containing 1% bovine serum albumin and 15 mM sodium azide.
免責聲明
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
未找到合适的产品?
试试我们的产品选型工具.
儲存類別代碼
10 - Combustible liquids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 1
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
Allyson G Hindle et al.
American journal of physiology. Regulatory, integrative and comparative physiology, 316(6), R704-R715 (2019-03-21)
Nitric oxide (NO) is a potent vasodilator, which improves perfusion and oxygen delivery during tissue hypoxia in terrestrial animals. The vertebrate dive response involves vasoconstriction in select tissues, which persists despite profound hypoxia. Using tissues collected from Weddell seals at
Staffan Hildebrand et al.
Communications biology, 5(1), 197-197 (2022-03-05)
The nitric oxide-cGMP (NO-cGMP) pathway is of outstanding importance for vascular homeostasis and has multiple beneficial effects in vascular disease. Neointimal hyperplasia after vascular injury is caused by increased proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs). However, the
Oxygen Binding and Redox Properties of the Heme in Soluble Guanylate Cyclase IMPLICATIONS FOR THE MECHANISM OF LIGAND DISCRIMINATION
Makino R, et al.
The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 286(18), 15678-15687 (2011)
Christopher J Mingone et al.
American journal of physiology. Heart and circulatory physiology, 294(3), H1244-H1250 (2008-01-08)
This study examines in endothelium-denuded bovine pulmonary arteries the effects of increasing heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) activity on relaxation and soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC) activation by nitric oxide (NO). A 24-h organ culture with 0.1 mM cobalt chloride (CoCl2) or 30
S Iino et al.
Neurogastroenterology and motility : the official journal of the European Gastrointestinal Motility Society, 21(5), 542-550 (2009-01-30)
Nitric oxide (NO) is an inhibitory signalling molecule in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract that is released from neurons and from leucocytes during inflammation. NO stimulates soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC), elevates cyclic guanosine 3',5'-monophospate (cGMP), and subsequently activates cGMP-dependent protein kinase
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门