推荐产品
重組細胞
expressed in Streptomyces lividans
形狀
lyophilized solid
比活性
≥18 unit/mg solid
分子量
~37 kDa by SDS-PAGE
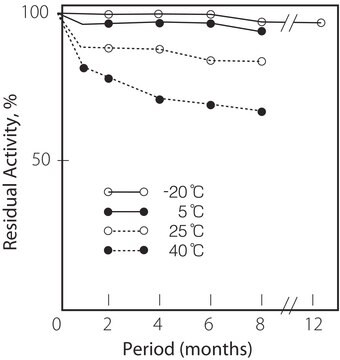
儲存溫度
−20°C
應用
此胆固醇脱氢酶的序列来自诺卡氏菌(Nocardia sp.),通过变铅青链霉菌(Streptomyces lividans)表达。胆固醇脱氢酶(诺卡氏菌)已用于制备安培型胆固醇生物传感器,检测生物样品中的胆固醇,并用于研究常染色体隐性遗传性高胆固醇血症磷酸酪氨酸结合域与低密度脂蛋白(LDL)受体尾部复合体的原子结构。胆固醇脱氢酶(诺卡氏菌)还用于研究Ras纳米簇在膜结构域中的组织、动态和解离。
用于测定血清胆固醇的酶
生化/生理作用
胆固醇脱氢酶(CDH)是NAD(P)依赖性微生物脱氢酶,可氧化胆固醇的3-β-羟基生成胆甾烯-4-烯-3-酮。SDS-PAGE法测定的蛋白分子量为37kDa。pH是4.5。
胆固醇脱氢酶(CDH)是依赖烟酰胺腺嘌呤二核苷酸磷酸(NAD(P))的微生物脱氢酶,可氧化胆固醇的3-β-羟基生成胆甾烯-4-烯-3-酮。相比基于胆固醇氧化酶的分析方法,CDH可更加轻松地直接定量测定胆固醇。
單位定義
一个单位将在pH 8.5和25℃下,每分钟产生1.0 μmole胆甾烯-4-烯-3-酮。
外觀
以冻干粉形式提供
訊號詞
Danger
危險聲明
危險分類
Resp. Sens. 1
儲存類別代碼
11 - Combustible Solids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 3
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
個人防護裝備
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Lorant Janosi et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 109(21), 8097-8102 (2012-05-09)
Recent experiments have shown that membrane-bound Ras proteins form transient, nanoscale signaling platforms that play a crucial role in high-fidelity signal transmission. However, a detailed characterization of these dynamic proteolipid substructures by high-resolution experimental techniques remains elusive. Here we use
Takeshi Nomura et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 109(22), 8770-8775 (2012-05-16)
Mechanosensitive (MS) channels of small (MscS) and large (MscL) conductance are the major players in the protection of bacterial cells against hypoosmotic shock. Although a great deal is known about structure and function of these channels, much less is known
Hay Dvir et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 109(18), 6916-6921 (2012-04-18)
Hypercholesterolemia, high serum cholesterol in the form of LDL, is a major risk factor for atherosclerosis. LDL is mostly degraded in the liver after its cellular internalization with the LDL receptor (LDLR). This clathrin-mediated endocytosis depends on the protein autosomal
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门