所有图片(4)
About This Item
经验公式(希尔记法):
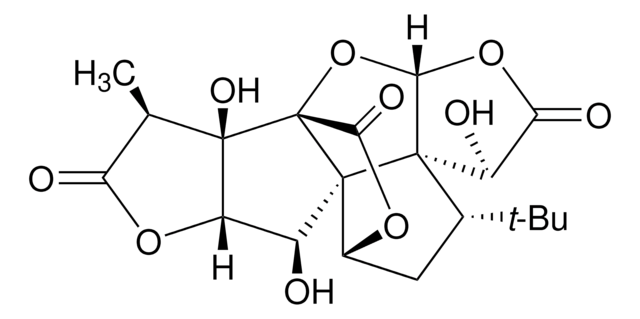
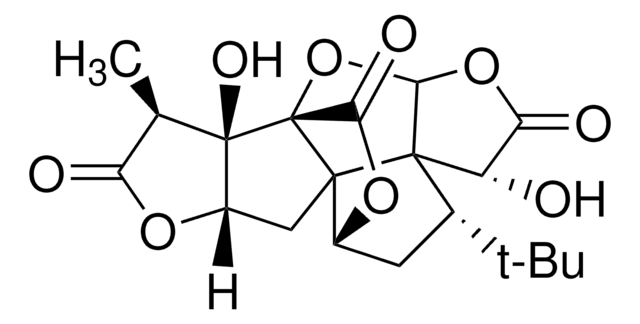
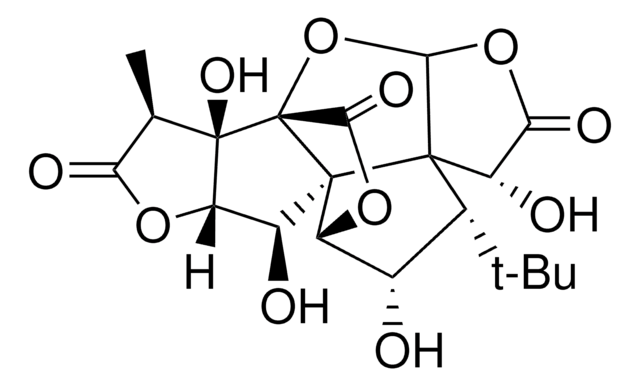
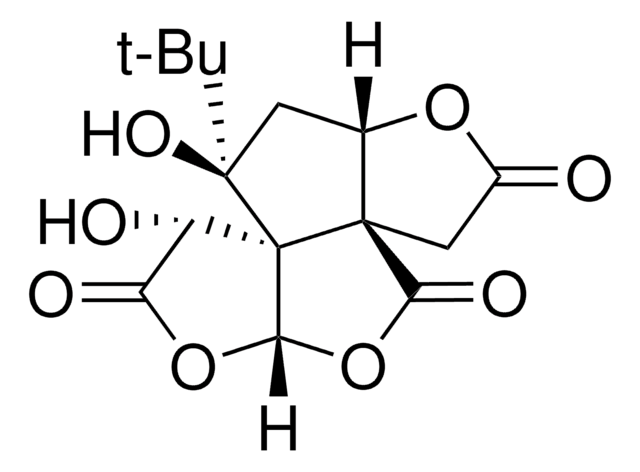
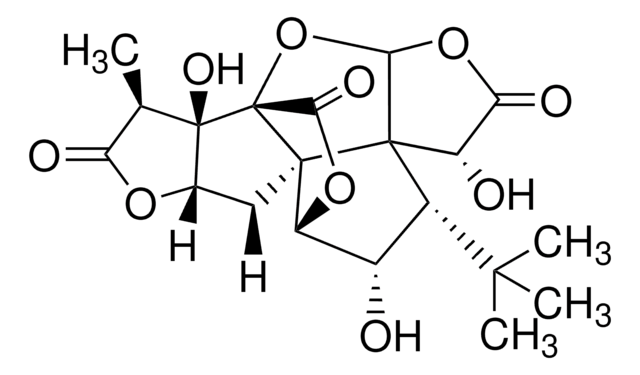
C15H18O8
CAS号:
分子量:
326.30
MDL號碼:
分類程式碼代碼:
85151701
PubChem物質ID:
NACRES:
NA.28
推荐产品
生物源
plant leaves (Ginkgo biloba)
品質等級
化驗
≥93% (HPLC)
形狀
powder
技術
HPLC: suitable
顏色
white
儲存溫度
−20°C
SMILES 字串
CC(C)(C)[C@]1(O)CC2OC(=O)C[C@@]23C(=O)OC4OC(=O)[C@H](O)[C@]134
InChI
1S/C15H18O8/c1-12(2,3)14(20)4-6-13(5-7(16)21-6)10(19)23-11-15(13,14)8(17)9(18)22-11/h6,8,11,17,20H,4-5H2,1-3H3/t6-,8-,11-,13-,14+,15+/m0/s1
InChI 密鑰
MOLPUWBMSBJXER-YDGSQGCISA-N
一般說明
Bilobalide is a biologically active terpenic trilactone (terpenoid) extracted from Ginkgo biloba. It is synthesized from geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate (GGPP).
應用
(-)-Bilobalide from Ginkgo biloba leaves has been used as a reference substance to study the antimicrobial activity of different fractions of G.biloba leaves against a number of Gram-positive and negative bacteria and yeasts.
生化/生理作用
Bilobalide is an inducer of cytochrome P450 enzymes CYP3A1 and CYP1A2. It exhibits neuroprotective, anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidative and anti-apoptotic properties. Bilobalide, a γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) AA-rho, 5-hydroxytryptamine type 3 (5-HT(3)) receptor antagonist, may be used to study the function of these receptors in the brain processes such as cognition and memory. It serves as a specific platelet-activating factor receptor antagonist, which helps in the treatment of cardiovascular (Alzheimer′s disease) and cerebrovascular diseases.
Bioactive terpenoid found in Ginkgo biloba.
儲存類別代碼
11 - Combustible Solids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 3
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
個人防護裝備
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
其他客户在看
Induction of cytochrome P450 3A by the Ginkgo biloba extract and bilobalides in human and rat primary hepatocytes
Zhou SF, et al.
Drug Metabolism Letters, 2(1), 60-66 (2008)
Antimicrobial investigation of semipurified fractions of Ginkgo biloba leaves
Mazzanti G, et al.
Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 71(1-2), 83-88 (2000)
Protective and therapeutic role of Bilobalide in cuprizone-induced demyelination
Sui RX, et al.
International Immunopharmacology, 66, 69-81 (2019)
Molecular cloning, characterization, and functional analysis of acetyl-CoA C-acetyltransferase and mevalonate kinase genes involved in terpene trilactone biosynthesis from Ginkgo biloba
Chen Q, et al.
Molecules (Basel), 22(1), 74-74 (2017)
Flaubert Tchantchou et al.
Journal of Alzheimer's disease : JAD, 18(4), 787-798 (2009-08-08)
Loss of synapses has been correlated with dementia in Alzheimer's disease (AD) as an early event during the disease progression. Hence, synaptogenesis and neurogenesis in adulthood could serve as a therapeutic target for the prevention and treatment of AD. Recently
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门