推荐产品
生物源
rabbit
共軛
unconjugated
抗體表格
affinity isolated antibody
抗體產品種類
primary antibodies
無性繁殖
polyclonal
形狀
buffered aqueous solution
分子量
antigen ~150 kDa
物種活性
rat, human (predicted), mouse
加強驗證
recombinant expression
Learn more about Antibody Enhanced Validation
濃度
~1 mg/mL
技術
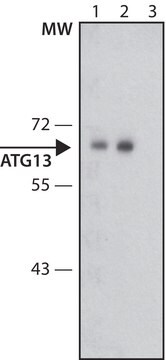
western blot: 0.5-1.0 μg/mL using whole extracts of HEK-293T cells expressing mouse ULK1
western blot: 3-6 μg/mL using whole extracts of rat PC12
UniProt登錄號
運輸包裝
dry ice
儲存溫度
−20°C
目標翻譯後修改
unmodified
基因資訊
human ... ULK1(8408)
mouse ... Ulk1(22241)
rat ... Ulk1(360827)
一般說明
Atg1是一种自噬蛋白,在酵母中作为丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶调节自噬体的形成。在哺乳动物中,Atg1是ULK1。
Unc-51样自噬激活激酶1(ULK1)基因位于人染色体12q24.33上。
特異性
Atg1/ULK1抗体可识别大鼠和小鼠Atg1/ULK1。
免疫原
对应于通过半胱氨酸残基与KLH偶联的小鼠Atg1/ULK1氨基酸的合成肽。与大鼠中的相应序列相同,与人的相应序列相差3个氨基酸。
應用
兔抗Atg1/ULK1抗体还可用于蛋白印迹和免疫组化染色。
生化/生理作用
Unc-51样自噬激活激酶1(ULK1)调节干扰素(IFN)的自噬启动和先天免疫。ULK1对神经元发育至关重要。它对小脑颗粒神经元的神经突伸长和分化至关重要。该基因的突变与潜伏性结核分枝杆菌感染(LTBI)有关。
外觀
溶于含有15 mM叠氮化钠的0.01 M磷酸盐缓冲液(pH 7.4)。
儲存和穩定性
如需连续使用,可在2-8°C下保存一个月。对于长期储存,可将工作浓度的分装品冷冻。不建议反复冻融。如果长期储存时出现轻微混浊,使用前通过离心澄清溶液。如果在12小时内未使用,则应丢弃工作稀释样品。
免責聲明
除非我们的产品目录或产品附带的其他公司文档另有说明,否则我们的产品仅供研究使用,不得用于任何其他目的,包括但不限于未经授权的商业用途、体外诊断用途、离体或体内治疗用途或任何类型的消费或应用于人类或动物。
未找到合适的产品?
试试我们的产品选型工具.
儲存類別代碼
10 - Combustible liquids
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
個人防護裝備
Eyeshields, Gloves, multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US)
其他客户在看
Beyond autophagy: New roles for ULK1 in immune signaling and interferon responses
Saleiro D, et al.
Cytokine & Growth Factor Reviews, 29, 17-22 (2016)
Gene responsible for mitochondrial myopathy and sideroblastic anemia (MSA) maps to chromosome 12q24. 33
Casas K, et al.
American Journal of Medical Genetics. Part A, 127(1), 44-49 (2004)
Ryan C Scott et al.
Current biology : CB, 17(1), 1-11 (2007-01-09)
To survive starvation and other forms of stress, eukaryotic cells undergo a lysosomal process of cytoplasmic degradation known as autophagy. Autophagy has been implicated in a number of cellular and developmental processes, including cell-growth control and programmed cell death. However
Nao Hosokawa et al.
Molecular biology of the cell, 20(7), 1981-1991 (2009-02-13)
Autophagy is an intracellular degradation system, by which cytoplasmic contents are degraded in lysosomes. Autophagy is dynamically induced by nutrient depletion to provide necessary amino acids within cells, thus helping them adapt to starvation. Although it has been suggested that
Noboru Mizushima et al.
Nature cell biology, 12(9), 823-830 (2010-09-03)
It has been known for many decades that autophagy, a conserved lysosomal degradation pathway, is highly active during differentiation and development. However, until the discovery of the autophagy-related (ATG) genes in the 1990s, the functional significance of this activity was
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门