推荐产品
形狀
solution
品質等級
用途
sufficient for 30 tests
包裝
pkg of 3 × 550 μL
製造商/商標名
Roche
顏色
colorless
溶解度
water: miscible
儲存溫度
−20°C
一般說明
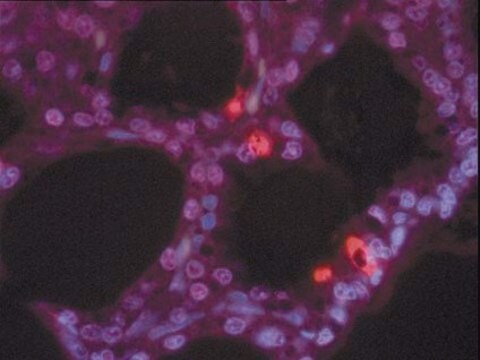
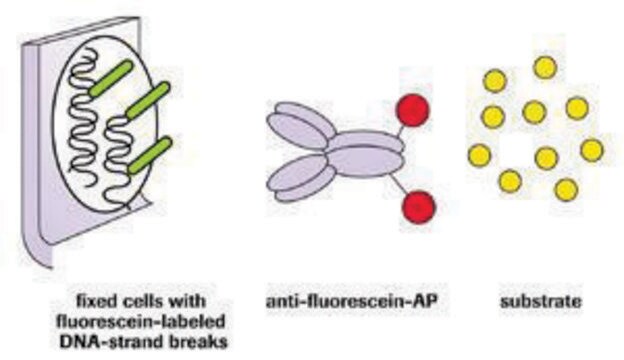
核苷酸标记混合物 (TUNEL 标记)包含荧光素-dUTP 和 -dNTP,两者都需要进行 TUNEL (末端脱氧核苷酸转移酶 dUTP 缺口末端标记)反应以检测原位细胞凋亡。核苷酸标记混合物与 TUNEL 酶一起用于制备 TUNEL 反应混合物。该反应混合物用于标记 DNA 链断裂,用于检测和量化细胞和组织中单细胞水平的凋亡细胞死亡。
應用
TUNEL标记混合物已被用于通过TUNEL(末端脱氧核苷酸转移酶 dUTP 缺口末端标记)测定法和通过 TUNEL 方法的 DNA 缺口末端标记测定细胞凋亡。
核苷酸标记混合物 (TUNEL 标记 包含荧光素-dUTP 和 -dNTP,两者都需要进行 TUNEL 反应以检测原位细胞凋亡。核苷酸标记混合物与 TUNEL 酶一起用于制备 TUNEL 反应混合物。该反应混合物用于标记 DNA 链断裂,用于检测和量化细胞和组织中单细胞水平的凋亡细胞死亡。
準備報告
工作溶液:TUNEL标记与 TUNEL 酶一起用于制备 TUNEL 反应混合物。
一次测试:使用前混合45 μl TUNEL标记和 5 μl TUNEL 酶。对于阴性对照,仅使用 50μl/测试 TUNEL 标签。
储存条件(工作溶液):注意:TUNEL 反应混合物(1次测试用45μ 升 TUNEL 标记和 5μl TUNEL 酶)应在使用前制备,不应储存。将TUNEL反应混合物置于冰上直至使用。
一次测试:使用前混合45 μl TUNEL标记和 5 μl TUNEL 酶。对于阴性对照,仅使用 50μl/测试 TUNEL 标签。
储存条件(工作溶液):注意:TUNEL 反应混合物(1次测试用45μ 升 TUNEL 标记和 5μl TUNEL 酶)应在使用前制备,不应储存。将TUNEL反应混合物置于冰上直至使用。
其他說明
仅用于生命科学研究。不用于诊断操作。
訊號詞
Danger
危險聲明
危險分類
Aquatic Chronic 2 - Carc. 1B Inhalation
儲存類別代碼
6.1D - Non-combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic hazardous materials or hazardous materials causing chronic effects
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 3
閃點(°F)
does not flash
閃點(°C)
does not flash
其他客户在看
Liang Liu et al.
Frontiers in oncology, 11, 648152-648152 (2021-08-13)
Glioma is the most common primary tumour of the central nervous system and is considered one of the greatest challenges for neurosurgery. Mounting evidence has shown that lncRNAs participate in various biological processes of tumours, including glioma. This study aimed
Ding Tian et al.
Cell death & disease, 11(7), 526-526 (2020-07-15)
Dysfunction of endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) is a key factor in vascular complications of diabetes mellitus. Although the roles of microRNAs and circular RNAs in regulating cell functions have been thoroughly studied, their role in regulating autophagy and apoptosis of
Karl J Wahlin et al.
PloS one, 8(11), e79140-e79140 (2013-11-19)
Vertebrate genomes undergo epigenetic reprogramming during development and disease. Emerging evidence suggests that DNA methylation plays a key role in cell fate determination in the retina. Despite extensive studies of the programmed cell death that occurs during retinal development and
Yan Yang et al.
Neural regeneration research, 15(3), 464-472 (2019-10-02)
Mitochondrial dysfunction in neurons has been implicated in hypoxia-ischemia-induced brain injury. Although mesenchymal stem cell therapy has emerged as a novel treatment for this pathology, the mechanisms are not fully understood. To address this issue, we first co-cultured 1.5 ×
Sophie A Montandon et al.
EvoDevo, 5, 33-33 (2015-02-24)
Mammals exhibit a remarkable variety of phenotypes and comparative studies using novel model species are needed to uncover the evolutionary developmental mechanisms generating this diversity. Here, we undertake a developmental biology and numerical modeling approach to investigate the development of
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门