推荐产品
product name
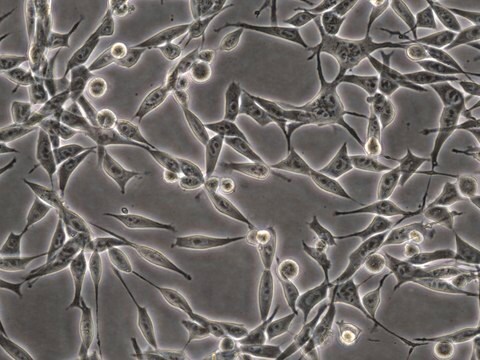
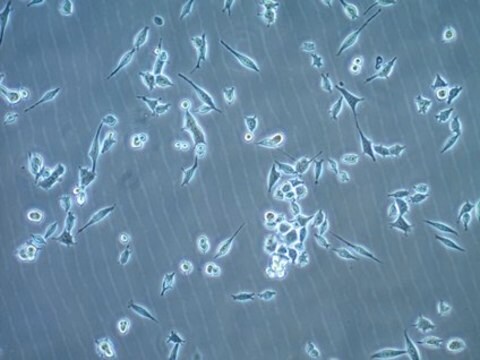
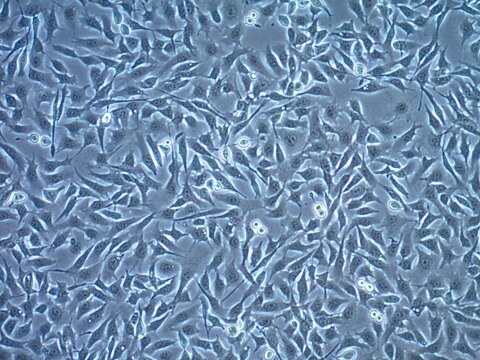
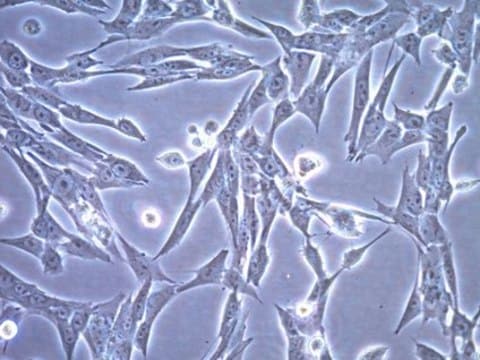
ID8小鼠卵巢表面上皮细胞系, ID8 mouse ovarian surface epithelial cell line is frequently used as a syngeneic mouse model for human ovarian cancer.
生物源
mouse
技術
cell culture | mammalian: suitable
運輸包裝
liquid nitrogen
一般說明
ID8是从晚期传代的C57BL/6小鼠卵巢表面上皮细胞(MOSEC)中建立的10个克隆系之一。将10个克隆系中的每一个腹膜内注射到C57BL/6小鼠中,导致腹膜肿瘤和腹水的形成。在10个克隆系中,ID8表现出最高的肿瘤负荷。 ID8细胞系是高度公开且特征明确的细胞系,经常用作卵巢癌的同系小鼠模型。
卵巢癌是女性癌症相关死亡的第四大主要原因。 该疾病通常在后期被诊断出,并在整个腹膜腔中检测到肿瘤。大约90%的卵巢肿瘤起源于卵巢表面上皮细胞。 人和小鼠卵巢表面上皮细胞(OSE)已被分离并用于开发卵巢癌模型。 这些模型通常涉及将人/小鼠OSE细胞皮下、腹膜内或原位注射到免疫缺陷小鼠中。 这些模型的一个共同缺点是宿主小鼠中没有完整的免疫系统。
2000年,报道了具有免疫能力的卵巢癌同系小鼠模型。发现从C57BL/6小鼠分离的小鼠卵巢表面上皮细胞(MOSEC)在体外长时间传代后自发转化为恶性致瘤细胞。 晚期传代MOSEC失去了经典的“鹅卵石”接触抑制的体外特性,使人联想到正常的上皮细胞,而是以指示转化细胞的多层细胞簇生长。 腹膜内注射晚期传代的MOSEC到无胸腺和正常,免疫完整的同系C57BL/6小鼠中会在整个腹腔内产生肿瘤,就像在患有III期和IV期癌症的女性中观察到的那样。 因此,MOSEC是有用的同系小鼠模型,用于研究免疫系统在卵巢癌的建立和发展中的作用。
2000年,报道了具有免疫能力的卵巢癌同系小鼠模型。发现从C57BL/6小鼠分离的小鼠卵巢表面上皮细胞(MOSEC)在体外长时间传代后自发转化为恶性致瘤细胞。 晚期传代MOSEC失去了经典的“鹅卵石”接触抑制的体外特性,使人联想到正常的上皮细胞,而是以指示转化细胞的多层细胞簇生长。 腹膜内注射晚期传代的MOSEC到无胸腺和正常,免疫完整的同系C57BL/6小鼠中会在整个腹腔内产生肿瘤,就像在患有III期和IV期癌症的女性中观察到的那样。 因此,MOSEC是有用的同系小鼠模型,用于研究免疫系统在卵巢癌的建立和发展中的作用。
品質
• 每小瓶含有≥ 1X106个活细胞。
• Charles River动物诊断服务通过小鼠Essential CLEAR小组对细胞进行传染病检测,结果为阴性。
• 通过Charles River动物诊断服务的污染透明小组评估,证实细胞为小鼠来源,对大鼠、中国仓鼠、金色黄叙利亚仓鼠、人和非人灵长类动物(NHP)的种间污染物呈阴性。
• 细胞对支原体污染呈阴性
• Charles River动物诊断服务通过小鼠Essential CLEAR小组对细胞进行传染病检测,结果为阴性。
• 通过Charles River动物诊断服务的污染透明小组评估,证实细胞为小鼠来源,对大鼠、中国仓鼠、金色黄叙利亚仓鼠、人和非人灵长类动物(NHP)的种间污染物呈阴性。
• 细胞对支原体污染呈阴性
其他說明
根据产品文件中详述的“学术使用协议”的条款,本产品预期仅用于销售和销售给学术机构,以供内部学术研究使用。有关任何其他用途的信息,请联系licensing@emdmillipore.com。
儲存類別代碼
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 1
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
James Greenaway et al.
Gynecologic oncology, 108(2), 385-394 (2007-11-27)
Ovarian cancer is the fourth leading cause of cancer-related deaths among women and is among the least understood of all cancers. The objective of this study was to determine the effect of ovarian epithelial and stromal cell interaction in a
K F Roby et al.
Carcinogenesis, 21(4), 585-591 (2000-04-07)
Mouse ovarian surface epithelial cells (MOSEC) were obtained from virgin, mature mice by mild trypsinization and were repeatedly passaged in vitro. Early passage cells (<20 passages) exhibited a cobblestone morphology and contact inhibition of growth. After approximately 20 passages in
Zixiang Wang et al.
Nature communications, 13(1), 6246-6246 (2022-10-22)
Dysregulated expression of splicing factors has important roles in cancer development and progression. However, it remains a challenge to identify the cancer-specific splicing variants. Here we demonstrate that spliceosome component BUD31 is increased in ovarian cancer, and its higher expression
Li Jiang et al.
Frontiers in immunology, 9, 2927-2927 (2019-01-09)
Fatty acid synthase (FASN), the key metabolic enzyme of de novo lipogenesis, provides proliferative and metastatic capacity directly to cancer cells have been described. However, the impact of aberrant activation of this lipogenic enzyme on host anti-tumor immune milieu remains
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门