推荐产品
生物源
mouse
品質等級
抗體表格
purified immunoglobulin
抗體產品種類
primary antibodies
無性繁殖
4-1a, monoclonal
物種活性
human, mouse, bovine, rat
技術
ELISA: suitable
immunocytochemistry: suitable
immunofluorescence: suitable
immunohistochemistry: suitable (paraffin)
western blot: suitable
同型
IgG2aκ
NCBI登錄號
UniProt登錄號
運輸包裝
wet ice
目標翻譯後修改
unmodified
基因資訊
human ... LPL(4023)
一般說明
Lipoprotein lipase (EC 3.1.1.34; UniProt P06858; also known as hLPL, LPL) is encoded by the LPL (also known as LIPD) gene (Gene ID 4023) in human. Lipoprotein lipase (LPL) catalyzes the hydrolysis of triglycerides in plasma lipoproteins. LPL is produced by adipocytes and myocytes and secreted into the interstitial spaces, where it is bound by GPIHBP1 (a glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored protein of capillary endothelial cells) and shuttled to the luminal face of capillaries. The GPIHBP1–LPL complex is crucial for the binding of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins (TRLs) to endothelial cells and the subsequent lipolytic processing of TRLs. TRLs bind only the LPL-GPIHBP1 complex, but not GPIHBP1 alone, on the cell surface. A deficiency of either protein results in severe hypertriglyceridemia (chylomicronemia) and impaired delivery of lipid nutrients to parenchymal cells. LPL is produced with a signal peptide sequence (a.a. 1-27), the removal of which yields the mature 448-amino acid (a.a. 28-475) enzyme containing a PLAT (Polycystin-1, Lipoxygenase, Alpha-Toxin) domain (a.a. 341-464) and a heparin-binding domain (a.a. 346-441).
特異性
Clone 4-1a binds human and bovine LPL, as well as GPIHBP1-bound LPL, but not human hepatic lipase. Clone 4-1a does not inhibit LPL catalytic activity or LPL heparin interaction, nor does clone 4-1a compete against triglyceride-rich lipoproteins (LRLs) for bining GPIHBP1-LPL complex (Bensadoun, A., et al. (2014). Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1841(7):970-976).
免疫原
Epitope: Near the N-terminus of mature LPL.
Purified human plasma lipoprotein lipase/LPL.
應用
Anti-Lipoprotein Lipase/LPL Antibody, clone 4-1a is an antibody against Lipoprotein Lipase/LPL for use in Immunohistochemistry (Paraffin), Western Blotting, ELISA, Immunocytochemistry, Immunofluorescence.
Immunohistochemistry Analysis: A 1:50 dilution from a representative lot detected lipoprotein lipase/LPL immunoreactivity in human pancreas, human skeletal muscle, and rat heart tissue sections.
Western Blotting Analysis: A representative lot detected human plasma lipoprotein lipase (LPL) and bovine milk LPL by Western blotting. Clone 4-1a exhibited much reduced binding to murine or chicken LPL, and failed to detect human hepatic lipase (hHL) (Bensadoun, A., et al. (2014). Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1841(7):970-976).
Western Blotting Analysis: A representative lot detected recombinant wild-type human LPL (rhLPL), as well as rhLPL with mutated Gln3 & Arg4. Clone 4-1a failed to react with rhLPL with mutated Ile8 or Asp9, nor rhLPL with either a.a. 5-15 or aa.16-25 deletion (Bensadoun, A., et al. (2014). Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1841(7):970-976).
ELISA Analysis: A representative lot was employed as the capture antibody for the detection of human LPL by sandwich ELISA, using biotinylated clone 5D2 as the detcting antibody (Bensadoun, A., et al. (2014). Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1841(7):970-976).
Immunocytochemistry Analysis: A representative lot detected the binding of human LPL to CHO and CHL cells transfected to express surface GPIHBP1, but not to mock transfected cells or cells transfected to express GPIHBP1 C65S mutant. Clone 4-1a does not compete against triglyceride-rich lipoproteins (TRLs) for binding the LPL-GPIHBP1 complex on cell surface (Bensadoun, A., et al. (2014). Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1841(7):970-976).
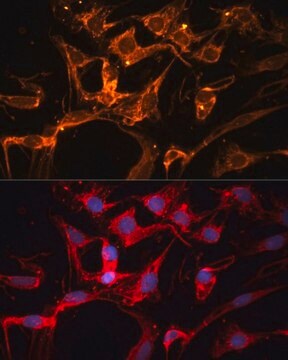
Immunofluorescence Analysis: A representative lot detected hLPL immunoreactivity associated with GPIHBP1 on capillary endothelial cells in OCT-embedded, methanol/acetone-fixed frozen skeletal muscle sections from mice expressing muscle-specific human LPL transgene. Much lower immunoreactivity of the endogenous mLPL was detected in skeletal muscle sections from non-transgenic mice (Bensadoun, A., et al. (2014). Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1841(7):970-976).
Note: Clone 4-1a exhibits much weaker affinity toward rat & murine LPL when compared with human LPL. Higher amount of sample loading (in Western blotting and ELISA) and/or high sensitivity detection method (e.g. HRP polymer or fluorescence detection in Western blotting and immunohistochemistry) is recommended when using this clone for detecting rat & murine LPL.
Western Blotting Analysis: A representative lot detected human plasma lipoprotein lipase (LPL) and bovine milk LPL by Western blotting. Clone 4-1a exhibited much reduced binding to murine or chicken LPL, and failed to detect human hepatic lipase (hHL) (Bensadoun, A., et al. (2014). Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1841(7):970-976).
Western Blotting Analysis: A representative lot detected recombinant wild-type human LPL (rhLPL), as well as rhLPL with mutated Gln3 & Arg4. Clone 4-1a failed to react with rhLPL with mutated Ile8 or Asp9, nor rhLPL with either a.a. 5-15 or aa.16-25 deletion (Bensadoun, A., et al. (2014). Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1841(7):970-976).
ELISA Analysis: A representative lot was employed as the capture antibody for the detection of human LPL by sandwich ELISA, using biotinylated clone 5D2 as the detcting antibody (Bensadoun, A., et al. (2014). Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1841(7):970-976).
Immunocytochemistry Analysis: A representative lot detected the binding of human LPL to CHO and CHL cells transfected to express surface GPIHBP1, but not to mock transfected cells or cells transfected to express GPIHBP1 C65S mutant. Clone 4-1a does not compete against triglyceride-rich lipoproteins (TRLs) for binding the LPL-GPIHBP1 complex on cell surface (Bensadoun, A., et al. (2014). Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1841(7):970-976).
Immunofluorescence Analysis: A representative lot detected hLPL immunoreactivity associated with GPIHBP1 on capillary endothelial cells in OCT-embedded, methanol/acetone-fixed frozen skeletal muscle sections from mice expressing muscle-specific human LPL transgene. Much lower immunoreactivity of the endogenous mLPL was detected in skeletal muscle sections from non-transgenic mice (Bensadoun, A., et al. (2014). Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1841(7):970-976).
Note: Clone 4-1a exhibits much weaker affinity toward rat & murine LPL when compared with human LPL. Higher amount of sample loading (in Western blotting and ELISA) and/or high sensitivity detection method (e.g. HRP polymer or fluorescence detection in Western blotting and immunohistochemistry) is recommended when using this clone for detecting rat & murine LPL.
Research Category
Signaling
Signaling
Research Sub Category
Lipid Metabolism & Weight Regulation
Lipid Metabolism & Weight Regulation
品質
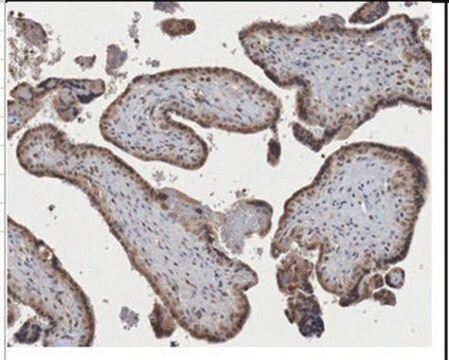
Evaluated by Immunohistochemistry in mouse heart tissue.
Immunohistochemistry Analysis: A 1:50 dilution of this antibody detected lipoprotein lipase/LPL immunoreactivity in mouse heart tissue sections.
Immunohistochemistry Analysis: A 1:50 dilution of this antibody detected lipoprotein lipase/LPL immunoreactivity in mouse heart tissue sections.
標靶描述
53.16 kDa (ProLPL) and 50.39 (Mature LPL) calculated. ~56 kDa observed (Bensadoun, A., et al. (2014). Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1841(7):970-976).
外觀
Protein G Purified
Format: Purified
Purified mouse monoclonal IgG2aκ antibody in buffer containing 0.1 M Tris-Glycine (pH 7.4), 150 mM NaCl with 0.05% sodium azide.
儲存和穩定性
Stable for 1 year at 2-8°C from date of receipt.
其他說明
Concentration: Please refer to lot specific datasheet.
免責聲明
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
未找到合适的产品?
试试我们的产品选型工具.
儲存類別代碼
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 1
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门