推荐产品
product name
High Sensitivity Human Amyloid β42 ELISA, This High Sensitivity Human Amyloid β42 ELISA is used to measure & quantify Amyloid β42 levels in Neuroscience research.
品質等級
物種活性
human
包裝
kit of 1 × 96 wells
參數
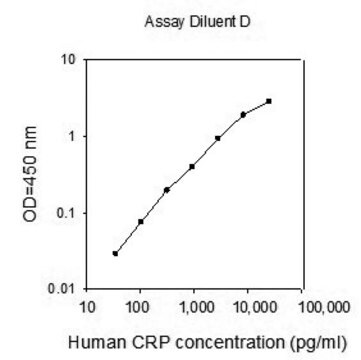
50 μL sample volume (Overnight assay)
assay range
sensitivity: 8.0 pg/mL
(50 μl sample size)
standard curve range: 16-500 pg/mL
技術
ELISA: suitable
輸入
sample type plasma (K2 EDTA)
sample type serum
sample type cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
應用
research use
檢測方法
colorimetric (450nm/590nm)
運輸包裝
wet ice
儲存溫度
2-8°C
基因資訊
human ... APP(351)
一般說明
Amyloid beta peptides have been implicated in the etiology of Alzheimer’s disease. Amyloid beta 40 is the most prominent peptide and Amyloid beta 42 is the neurotoxic form. The Amyloid beta 42/40-ratio (AB ratio) has been reported as a better indicator of the Alzheimer pathology. Millipore’s High Sensitivity Human Amyloid β42 ELISA kit is used for the measurement of Amyloid β42 in cerebrospinal fluid, cell culture supernatants, primary neurons and plasma in a 96-well format.
特異性
The Amyloid β42 ELISA (HS) uses monoclonal anti-Aβ antibodies with high selectivity for human Aβ. The capture antibody recognizes the C-terminal end of Amyloid β1-42, which causes a high selectivity for Aβ42. The cross-reactivity of the used antibodies to other Amyloid peptides was tested by ELISA and BIACORE and shows no significant cross-reactivity to Aβ1-38, Aβ1-39, Aβ1-40, Aβ1-43 and Aβ1-44.
應用
Research Category
Neuroscience
Neuroscience
Research Sub Category
Alzheimer′s Disease
Alzheimer′s Disease
This High Sensitivity Human Amyloid β42 ELISA is used to measure & quantify Amyloid β42 levels in Neuroscience research.
This assay requires 50 µl of sample and is an overnight assay.
Used to detect/quantify: Amyloid β42
儲存和穩定性
Components in the kit can be stored up to 2 weeks at 2-8°C
其他說明
Please contact Technical Service for linearity of dilution.
免責聲明
For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
訊號詞
Warning
危險聲明
危險分類
Aquatic Chronic 3 - Met. Corr. 1 - Skin Sens. 1
儲存類別代碼
8A - Combustible corrosive hazardous materials
Teresa Niccoli et al.
Current biology : CB, 26(17), 2291-2300 (2016-08-16)
Glucose hypometabolism is a prominent feature of the brains of patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD). Disease progression is associated with a reduction in glucose transporters in both neurons and endothelial cells of the blood-brain barrier. However, whether increasing glucose transport
Gunjan Manocha et al.
Current Alzheimer research, 15(12), 1123-1135 (2018-08-03)
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is associated with age-associated central nervous system degeneration and dementia. This decline in the function correlates with deposition of Aβ peptide containing plaques and associated reactive gliosis. The inflammatory phenotype of microglia, in particular, is often considered
Nataliya Golovyashkina et al.
Molecular neurodegeneration, 10, 60-60 (2015-11-07)
Dendritic simplification, a key feature of the neurodegenerative triad of Alzheimer's disease (AD) in addition to spine changes and neuron loss, occurs in a region-specific manner. However, it is unknown how changes in dendritic complexity are mediated and how they
Kendra L Puig et al.
Journal of Alzheimer's disease : JAD, 44(4), 1263-1278 (2014-11-20)
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disorder histologically characterized by amyloid-β (Aβ) protein accumulation and activation of associated microglia. Although these features are well described in the central nervous system, the process and consequences of Aβ accumulation in the enteric
Loukia Katsouri et al.
Neurobiology of aging, 34(4), 1105-1115 (2012-10-16)
Noradrenergic deficits have been described in the hippocampus and the frontal cortex of Alzheimer's disease brains, which are secondary to locus coeruleus degeneration. Locus coeruleus is the brain stem nucleus responsible for synthesis of noradrenaline and from where all noradrenergic
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门