推荐产品
生物源
rabbit
品質等級
抗體表格
serum
抗體產品種類
primary antibodies
無性繁殖
polyclonal
物種活性
human, mouse, rat
製造商/商標名
Chemicon®
技術
immunocytochemistry: suitable
immunohistochemistry: suitable
western blot: suitable
NCBI登錄號
UniProt登錄號
運輸包裝
dry ice
目標翻譯後修改
unmodified
基因資訊
human ... TPM4(7171)
特異性
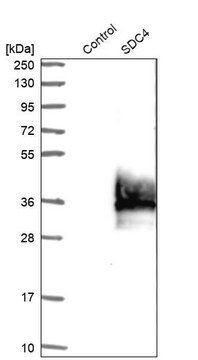
可识别原肌球蛋白4。
免疫原
对应于原肌球蛋白δ基因9d外显子的合成肽。
應用
可使用这种原肌球蛋白4抗体检测原肌球蛋白4,该抗体经验证可用于WB、IC、IH。
法律資訊
CHEMICON is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
未找到合适的产品?
试试我们的产品选型工具.
儲存類別代碼
11 - Combustible Solids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 1
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
Karim Chahed et al.
Clinica chimica acta; international journal of clinical chemistry, 388(1-2), 106-114 (2007-11-13)
Little emphasis has been placed today on the elucidation of protein alterations in male breast carcinogenesis. Protein extracts were subjected to both isoelectric focusing (IEF) and non-equilibrium pH gradient electrophoretic (NEPHGE) analyses. Differentially expressed proteins in tumor tissues were identified
Structural compartments within neurons: developmentally regulated organization of microfilament isoform mRNA and protein.
Hannan, A J, et al.
Molecular and Cellular Neurosciences, 11, 289-304 (1998)
Nicole Vlahovich et al.
Cell motility and the cytoskeleton, 65(1), 73-85 (2007-10-31)
The organisation of structural proteins in muscle into highly ordered sarcomeres occurs during development, regeneration and focal repair of skeletal muscle fibers. The involvement of cytoskeletal proteins in this process has been documented, with nonmuscle gamma-actin found to play a
Brooke K McMichael et al.
Experimental cell research, 314(3), 564-573 (2007-11-27)
Tropomyosins (Tms) are alpha-helical dimers that bind and stabilize actin microfilaments while regulating their accessibility to other actin-associated proteins. Four genes encode expression of over forty Tms, most of which are expressed in nonmuscle cells. In recent years, it has
Nicole Vlahovich et al.
Molecular biology of the cell, 20(1), 400-409 (2008-11-14)
The functional diversity of the actin microfilaments relies in part on the actin binding protein tropomyosin (Tm). The muscle-specific Tms regulate actin-myosin interactions and hence contraction. However, there is less known about the roles of the numerous cytoskeletal isoforms. We
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门