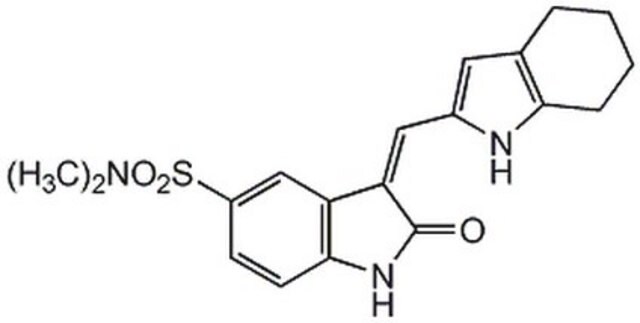
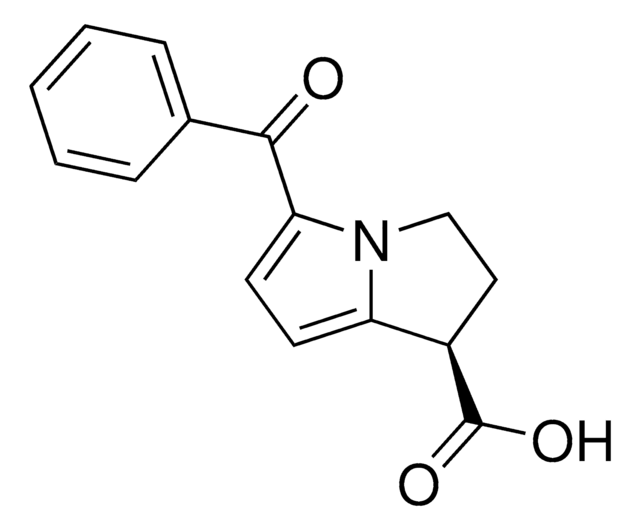
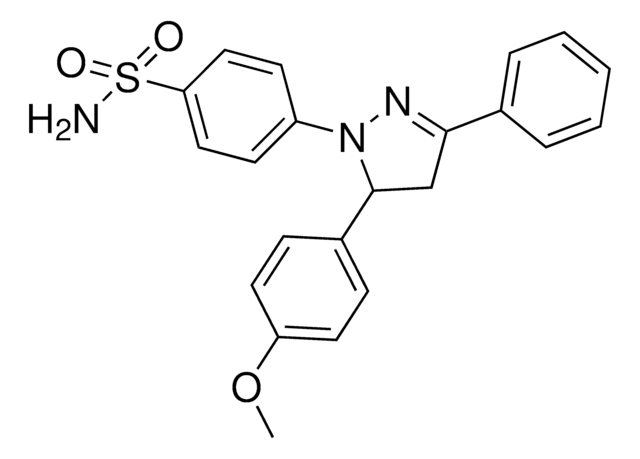
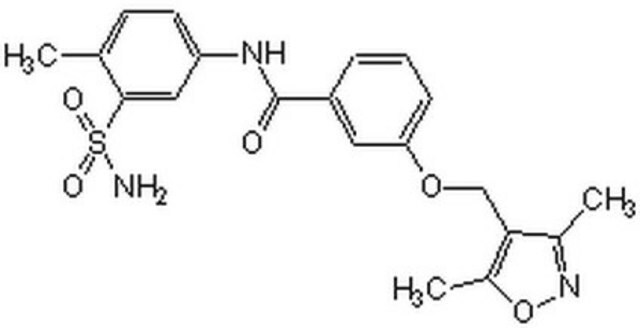
推荐产品
产品名称
Rac1抑制剂, Rac1 Inhibitor, CAS 1177865-17-6, is a cell-permeable, reversible inhibitor of Rac1 GDP/GTP exchange. Interferes with the interaction between Rac1 and Rac-specific GEFs Trio and Tiam1 (IC₅₀ ~50 µM).
品質等級
化驗
≥93% (HPLC)
形狀
lyophilized
製造商/商標名
Calbiochem®
儲存條件
OK to freeze
desiccated (hygroscopic)
protect from light
溶解度
water: 5 mg/mL
運輸包裝
ambient
儲存溫度
2-8°C
InChI
1S/C24H35N7.3ClH/c1-6-31(7-2)12-8-9-16(3)27-24-28-18(5)14-23(30-24)29-19-10-11-22-20(15-19)21(25)13-17(4)26-22;;;/h10-11,13-16H,6-9,12H2,1-5H3,(H2,25,26)(H2,27,28,29,30);3*1H
InChI 密鑰
CPUHORIUXPQCHW-UHFFFAOYSA-N
一般說明
一种细胞渗透性嘧啶化合物,通过干扰Rac1和Rac特异性GEF(鸟嘌呤核苷酸交换因子)Trio和Tiam1(IC50 ~50 µM)之间的相互作用,特异性和可逆地抑制Rac1 GDP/GTP交换活性。显示有效抑制NIH3T3和PC-3细胞中Rac1介导的细胞功能(有效剂量~50至100 μM)。对Cdc42或RhoA激活无影响,且不影响Rac1与BcrGAP或PAK1的相互作用。减少TRAP诱导和胶原刺激的血小板聚集(IC50分别为50 mM和64 mM)。
生化/生理作用
主要靶标
Rac1
Rac1
产物不与ATP竞争。
可逆性:是
细胞可渗透性:是
靶标IC50:针对Rac1 GDP/GTP交换活性约为50µM;针对TRAP诱导和胶原蛋白刺激的血小板聚集为50 mM和64 mM
包裝
用惰性气体包装
警告
毒性:致癌/致畸(D)
重構
复溶后,等分并冷冻保存(-20°C)。贮备溶液在-20°C下可稳定保存至多3个月。
其他說明
Dwivedi, S., et al. 2010.J. Translational Med.8, 128.
Desire, L., et al. 2005.J. Biol. Chem.280, 37516.
Gao, Y., et al. 2004.Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci. USA101, 7618.
Desire, L., et al. 2005.J. Biol. Chem.280, 37516.
Gao, Y., et al. 2004.Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci. USA101, 7618.
法律資訊
CALBIOCHEM is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
儲存類別代碼
11 - Combustible Solids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 3
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
其他客户在看
Shruthi Sriramkumar et al.
PloS one, 17(8), e0271584-e0271584 (2022-08-04)
Ovarian cancer (OC) is a lethal gynecological malignancy with a five-year survival rate of only 46%. Development of resistance to platinum-based chemotherapy is a common cause of high mortality rates among OC patients. Tumor and transcriptomic heterogeneity are drivers of
Kimia Ghaffari et al.
PLoS genetics, 17(3), e1009402-e1009402 (2021-03-20)
Impaired formation of the intrahepatic biliary network leads to cholestatic liver diseases, which are frequently associated with autoimmune disorders. Using a chemical mutagenesis strategy in zebrafish combined with computational network analysis, we screened for novel genes involved in intrahepatic biliary
Audrey Miller Williams et al.
eLife, 11 (2022-09-27)
For a group of cells to migrate together, each cell must couple the polarity of its migratory machinery with that of the other cells in the cohort. Although collective cell migrations are common in animal development, little is known about
Golnaz Morad et al.
International journal of molecular sciences, 21(11) (2020-06-03)
Breast cancer brain metastasis is a major clinical challenge and is associated with a dismal prognosis. Understanding the mechanisms underlying the early stages of brain metastasis can provide opportunities to develop efficient diagnostics and therapeutics for this significant clinical challenge.
Sonja Kühn et al.
Cell reports, 31(6), 107638-107638 (2020-05-14)
The enteroinvasive bacterium Shigella flexneri forces its uptake into non-phagocytic host cells through the translocation of T3SS effectors that subvert the actin cytoskeleton. Here, we report de novo actin polymerization after cellular entry around the bacterium-containing vacuole (BCV) leading to
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门