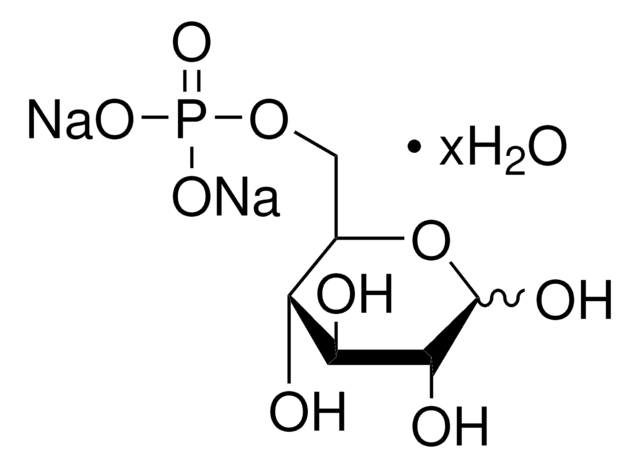
G7879
D-Glucose 6-phosphate sodium salt
≥98% (HPLC)
Synonym(s):
D(+)-Glucopyranose 6-phosphate sodium salt, G-6-P Na, Robison ester
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
synthetic (organic)
Quality Level
Assay
≥98% (HPLC)
form
crystalline
technique(s)
HPLC: suitable
color
white
useful pH range
4.0-5.0
mp
204 °C (dec.) (lit.)
solubility
water: 50 mg/mL, clear, colorless to very faintly yellow
cation traces
Na: 6.1-10.2% (anhydrous)
storage temp.
room temp
SMILES string
[Na+].O[C@@H]1O[C@H](COP(O)([O-])=O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O
InChI
1S/C6H13O9P.Na/c7-3-2(1-14-16(11,12)13)15-6(10)5(9)4(3)8;/h2-10H,1H2,(H2,11,12,13);/q;+1/p-1/t2-,3-,4+,5-,6-;/m1./s1
InChI key
ZALKNDISPIVVKC-WYRLRVFGSA-M
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Application
Biochem/physiol Actions
Caution
Other Notes
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Neoplastic cells are highly dependent on the de novo synthesis of nucleotides to maintain sufficient pools to support DNA replication and the production of RNA.
We presents an article about the Warburg effect, and how it is the enhanced conversion of glucose to lactate observed in tumor cells, even in the presence of normal levels of oxygen. Otto Heinrich Warburg demonstrated in 1924 that cancer cells show an increased dependence on glycolysis to meet their energy needs, regardless of whether they were well-oxygenated or not.
Protocols
Enzymatic Assay of Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.49)
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service