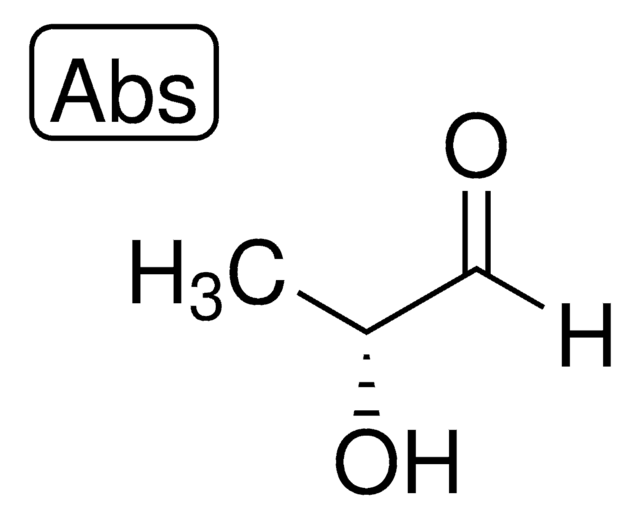
47014
L-Lactaldehyde solution
1 M in H2O
Synonym(s):
(2S)-2-Hydroxypropanal solution, (S)-2-Hydroxypropionaldehyde solution
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Recommended Products
Assay
≥95.0% (TLC)
Quality Level
optical purity
enantiomeric ratio: ≥98.0:2.0 (HPLC)
concentration
1 M in H2O
storage temp.
−20°C
SMILES string
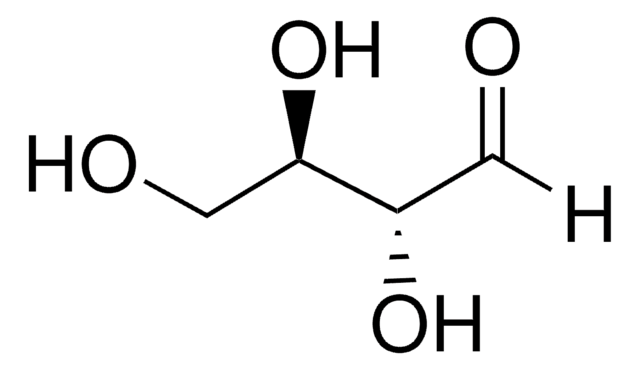
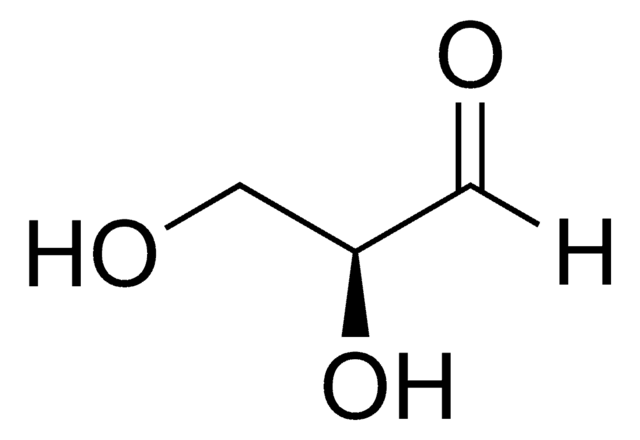
C[C@H](O)C([H])=O
InChI
1S/C3H6O2/c1-3(5)2-4/h2-3,5H,1H3/t3-/m0/s1
InChI key
BSABBBMNWQWLLU-VKHMYHEASA-N
Biochem/physiol Actions
L-Lactaldehyde is an intermediate metabolite in the pyruvate metabolism pathway and is irreversibly produced from pyruvaldehyde via the enzyme aldehyde reductase, which is then irreversibly converted to propylene glycol via aldehyde reductase.
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Lot/Batch Number
Don't see the Right Version?
If you require a particular version, you can look up a specific certificate by the Lot or Batch number.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Y Zhu et al.
Journal of bacteriology, 171(2), 862-867 (1989-02-01)
Catabolism of the six-carbon compound L-fucose results in formation of dihydroxyacetone phosphate (C-1-to-C-3 fragment) and L-lactaldehyde (C-4-to-C-6 fragment) as intermediates. The fate of lactaldehyde depends on the respiratory growth conditions. Aerobically, lactaldehyde is oxidized to L-lactate by an NAD-linked dehydrogenase
THE METABOLISM OF LACTALDEHYDE. VI. THE REDUCTION OF D- AND L-LACTALDEHYDE IN RAT LIVER.
S M TING et al.
Biochimica et biophysica acta, 89, 217-225 (1964-08-26)
Cristina Montella et al.
Journal of bacteriology, 187(14), 4957-4966 (2005-07-05)
The FucO protein, a member of the group III "iron-activated" dehydrogenases, catalyzes the interconversion between L-lactaldehyde and L-1,2-propanediol in Escherichia coli. The three-dimensional structure of FucO in a complex with NAD(+) was solved, and the presence of iron in the
L Baldomà et al.
Journal of bacteriology, 170(1), 416-421 (1988-01-01)
L-Lactaldehyde is a branching point in the metabolic pathway of L-fucose and L-rhamnose utilization. Under aerobic conditions, L-lactaldehyde is oxidized to L-lactate by the enzyme lactaldehyde dehydrogenase, while under anaerobic conditions, L-lactaldehyde is reduced to L-1,2-propanediol by the enzyme propanediol
Seiya Watanabe et al.
The FEBS journal, 275(20), 5139-5149 (2008-09-17)
Fungal Pichia stipitis and bacterial Azotobacter vinelandii possess an alternative pathway of L-rhamnose metabolism, which is different from the known bacterial pathway. In a previous study (Watanabe S, Saimura M & Makino K (2008) Eukaryotic and bacterial gene clusters related
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service