P4747
Anti-Potassium Channel KCa2.3, (C-term) (Small-conductance Ca2+-activated Potassium Channel 3) antibody produced in rabbit
affinity isolated antibody, lyophilized powder
Synonym(s):
Anti-SK3, Anti-SKCa3
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
conjugate:
unconjugated
application:
WB
clone:
polyclonal
species reactivity:
human, mouse, rat, pig
citations:
2
technique(s):
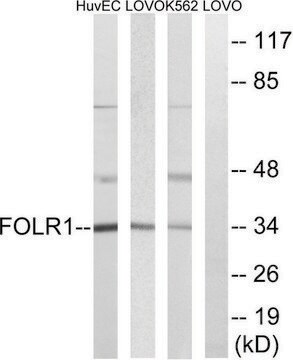
western blot: 1:200 using rat brain membranes
Recommended Products
biological source
rabbit
Quality Level
conjugate
unconjugated
antibody form
affinity isolated antibody
antibody product type
primary antibodies
clone
polyclonal
form
lyophilized powder
species reactivity
human, mouse, rat, pig
technique(s)
western blot: 1:200 using rat brain membranes
UniProt accession no.
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−20°C
target post-translational modification
unmodified
Gene Information
human ... KCNN3(3782)
mouse ... Kcnn3(140493)
rat ... Kcnn3(54263)
Immunogen
Synthetic peptide corresponding to amino acid residues 659-674 of human KCa2.3. This sequence has 100% homology in rat, mouse, pig.
Physical form
Lyophilized powder from phosphate buffered saline containing 1% bovine serum albumin and 0.05% sodium azide.
Not finding the right product?
Try our Product Selector Tool.
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
H Tomita et al.
Molecular psychiatry, 8(5), 524-535 (2003-06-17)
The small-conductance calcium-activated K(+) channel SK3 (SKCa3/KCNN3) regulates electrical excitability and neurotransmitter release in monoaminergic neurons, and has been implicated in schizophrenia, ataxia and anorexia nervosa. We have identified a novel SK3 transcript, SK3-1B that utilizes an alternative first exon
C Vergara et al.
Current opinion in neurobiology, 8(3), 321-329 (1998-08-04)
Calcium-activated potassium channels are fundamental regulators of neuronal excitability, participating in interspike interval and spike-frequency adaptation. For large-conductance calcium-activated potassium (BK) channels, recent experiments have illuminated the fundamental biophysical mechanisms of gating, demonstrating that BK channels are voltage gated and
Shaun L Sandow et al.
Journal of anatomy, 209(5), 689-698 (2006-10-26)
Activation of endothelial cell small- (S) and intermediate- (I) conductance calcium-activated potassium channels (K(Ca)) and current or molecular transfer via myoendothelial gap junctions underlies endothelium-derived hyperpolarization leading to vasodilation. The mechanism underlying the K(Ca) component of vasodilator activity and the
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service