SML0952
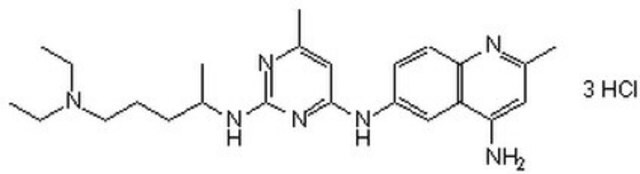
NSC23766 trihydrochloride
≥97% (HPLC)
Synonyme(s) :
N6-[2-(4-Diethylamino-1-methyl-butylamino)-6-methyl-pyrimidin-4-yl]-2-methyl-quinoline-4,6-diamine trihydrochloride
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Niveau de qualité
Essai
≥97% (HPLC)
Forme
powder
Conditions de stockage
desiccated
Couleur
white to beige
Solubilité
H2O: 10 mg/mL, clear
Température de stockage
−20°C
Chaîne SMILES
Cl.Cl.Cl.N(CCCC(Nc1nc(cc(n1)C)Nc2cc3c(nc(cc3N)C)cc2)C)(CC)CC
InChI
1S/C24H35N7.3ClH/c1-6-31(7-2)12-8-9-16(3)27-24-28-18(5)14-23(30-24)29-19-10-11-22-20(15-19)21(25)13-17(4)26-22;;;/h10-11,13-16H,6-9,12H2,1-5H3,(H2,25,26)(H2,27,28,29,30);3*1H
Clé InChI
CPUHORIUXPQCHW-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Application
Actions biochimiques/physiologiques
Caractéristiques et avantages
Code de la classe de stockage
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 3
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
Vous ne trouvez pas la bonne version ?
Si vous avez besoin d'une version particulière, vous pouvez rechercher un certificat spécifique par le numéro de lot.
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Contenu apparenté
Cyclic nucleotides, including cyclic AMP (cAMP), cyclic GMP (cGMP) and cyclic ADP-ribose, have been extensively studied as second messengers of intracellular events initiated by activation of GPCRs. cAMP modifies cell function in all eukaryotic cells, principally through the activation of cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA), but also through cAMP-gated ion channels and guanine nucleotide exchange factors directly activated by cAMP.
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique