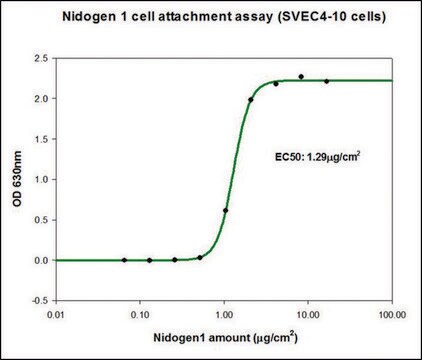
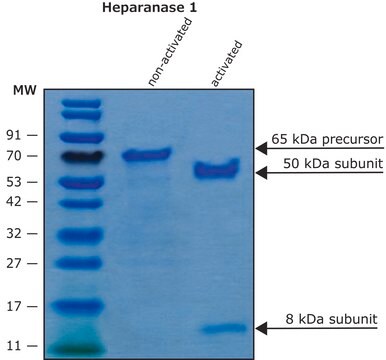
H4777
Heparan sulfate proteoglycan
≥400 μg/mL glycosaminoglycan
Synonyme(s) :
HSPG
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Source biologique
mouse (Engelbreth-Holm-Swarm mouse sarcoma basement membrane)
Niveau de qualité
Description
For cell culture use.
Isolated from basement membrane of Engelbreth-Holm-Swarm mouse sarcoma.
Solution in 50 mM Tris HCl, 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA, 0.1 mM PMSF, pH 7.4, containing ≥400 μg protein per ml.
Forme
solution
Poids mol.
≥400 kDa
Conditionnement
pkg of 0.1 mg
Concentration
≥400 μg/mL glycosaminoglycan
Technique(s)
cell culture | mammalian: suitable
Impuretés
≥100 μg/mL Uronic acid
Numéro d'accès NCBI
Numéro d'accès UniProt
Spécificité de la liaison
Peptide Source: Collagen Type IV
Peptide Source: Fibronectin
Peptide Source: Laminin
Conditions d'expédition
dry ice
Température de stockage
−20°C
Informations sur le gène
mouse ... Hspg2(15530)
Description générale
Application
- in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) and added to fresh citrated blood samples to achieve trauma-equivalent concentrations in a research study
- solid phase binding assay
- for fabrication of extracellular matrix (ECM) microarray slides
Actions biochimiques/physiologiques
Composants
Attention
Notes préparatoires
Code de la classe de stockage
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 3
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Équipement de protection individuelle
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
Recherchez un Certificats d'analyse (COA) en saisissant le numéro de lot du produit. Les numéros de lot figurent sur l'étiquette du produit après les mots "Lot" ou "Batch".
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Articles
There are five identified glycosaminoglycan chains (see Figure 1): Hyaluronan is not sulfated, but the other glycosaminoglycan chains contain sulfate substituents at various positions of the chain.
Glycosaminoglycans are large linear polysaccharides constructed of repeating disaccharide units.
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique