930962
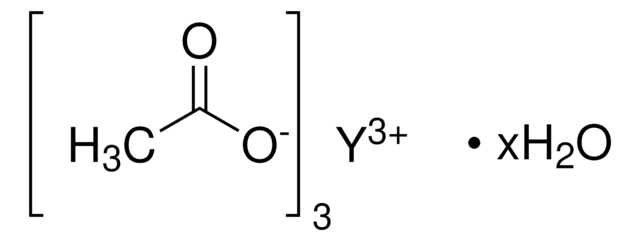
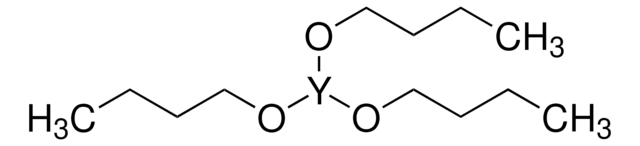
Yttrium(III) acetate tetrahydrate
99.99% trace rare earth metals basis
Synonyme(s) :
Acetic acid yttrium(3+) salt, Yttrium triacetate
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Niveau de qualité
Pureté
99.99% trace rare earth metals basis
Forme
powder
Impuretés
≤150 ppm trace rare earth metals
≤500 ppm trace metals
Pf
350 °C (Decomp.)
Solubilité
H2O: soluble (lit.)
Densité
1.5 g/cm3
Description générale
Application
A major application of high-purity yttrium acetate is in the synthesis of sodium yttrium fluoride (NaYF4) nanoparticles. Typically, in these syntheses, yttrium acetate is mixed with oleic acid in octadecene and heated to form Y(oleate)3, which is reacted with ammonium fluoride and sodium hydroxide in methanol at modest temperatures (e.g. 50 C) to form NaYF4 nanoparticles. This synthesis offers great control over particle size and crystallinity and allows for easy incorporation rare-earth metal dopants.
Lanthanide-doped NaYF4 nanoparticles are one of the most studied materials for up conversion. These nanoparticles, which can convert two photons of near-infrared (NIR) light into visible light, have important in-vivo applications because of the deep tissue penetration abilities of NIR. For example, these nanoparticles have been used for in-vivo Zn2+ optical sensing, in-vivo ratiometric sensing of lymphatic inflammation,, and in-vivo sensing of peroxynitrite.
Code de la classe de stockage
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 3
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
Désolés, nous n'avons pas de COA pour ce produit disponible en ligne pour le moment.
Si vous avez besoin d'assistance, veuillez contacter Service Clients
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique