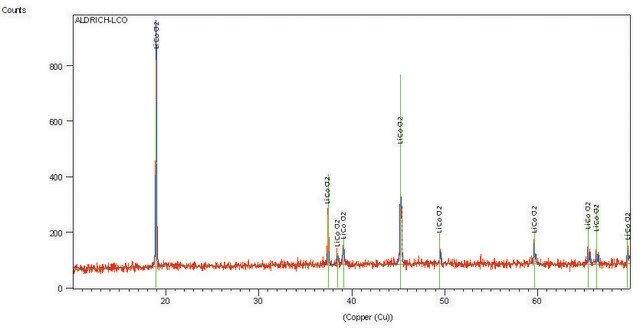
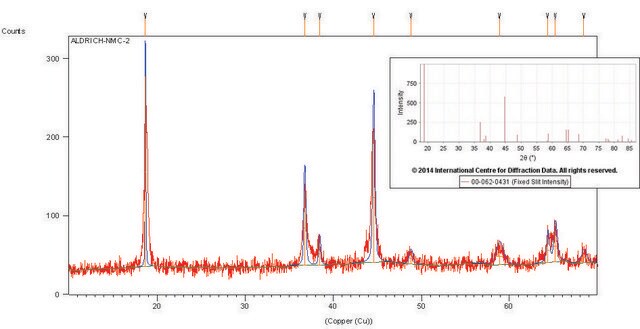
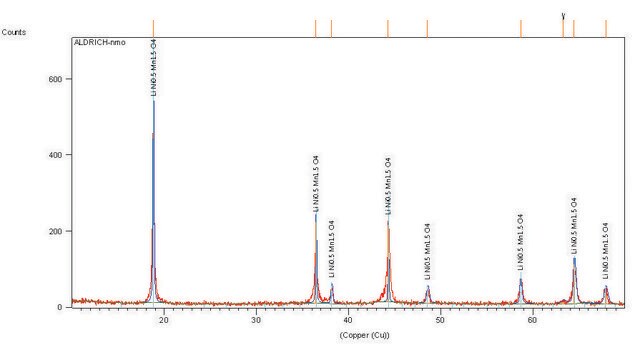
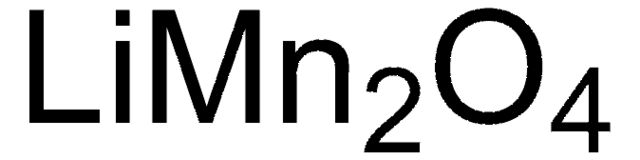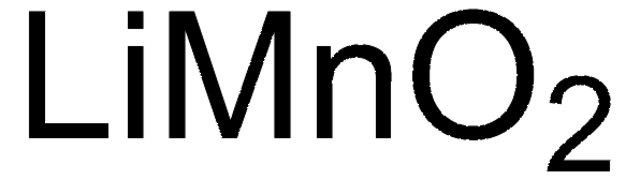757365
Lithium nickel dioxide
powder, <3 μm particle size (BET), ≥98% trace metals basis
Synonyme(s) :
LNO, Lithium nickel oxide, Lithium nickelate
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Qualité
battery grade
Niveau de qualité
Essai
≥98% trace metals basis
Forme
powder
Poids mol.
Mw 97.63 g/mol
Composition
LiNiO2
Taille des particules
<3 μm (BET)
Pf
>1,000 °C (lit.)
Densité
4.62 g/cm3 (lit.)
Application(s)
battery manufacturing
Chaîne SMILES
[Ni](=O)[O-].[Li+]
InChI
1S/Li.Ni.2O/q+1;;;-1
Clé InChI
VROAXDSNYPAOBJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Catégories apparentées
Description générale
Application
Informations légales
Produit(s) apparenté(s)
Mention d'avertissement
Danger
Mentions de danger
Conseils de prudence
Classification des risques
Carc. 1A Inhalation - Skin Sens. 1 - STOT RE 1
Code de la classe de stockage
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 3
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Listes réglementaires
Les listes réglementaires sont principalement fournies pour les produits chimiques. Seules des informations limitées peuvent être fournies ici pour les produits non chimiques. L'absence d'indication signifie qu'aucun des composants n'est répertorié. Il incombe à l'utilisateur de s'assurer de l'utilisation sûre et légale du produit.
EU REACH Annex XVII (Restriction List)
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Articles
Professor Qiao’s laboratory lays out recent advances in conversion type lithium metal fluoride batteries. This review explores key concepts in developing electrochemically stable microstructures for wide Li-ion insertion channels.
Discover more about advancements being made to improve energy density of lithium ion battery materials.
Li-ion batteries are currently the focus of numerous research efforts with applications designed to reduce carbon-based emissions and improve energy storage capabilities.
The critical technical challenges associated with the commercialization of electric vehicle batteries include cost, performance, abuse tolerance, and lifespan.
Global Trade Item Number
| Référence | GTIN |
|---|---|
| 757365-10G | 4061833433126 |
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique