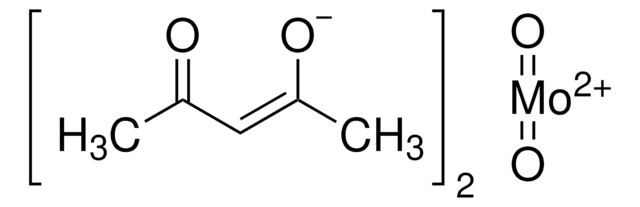
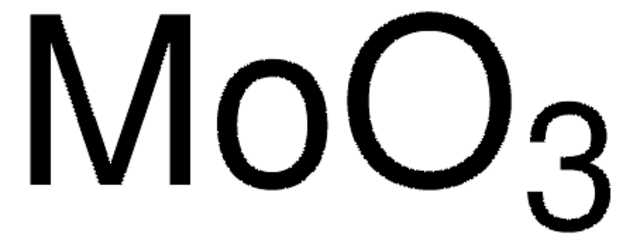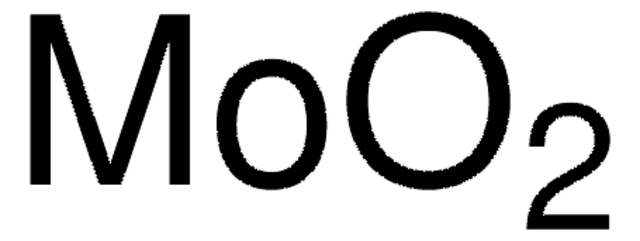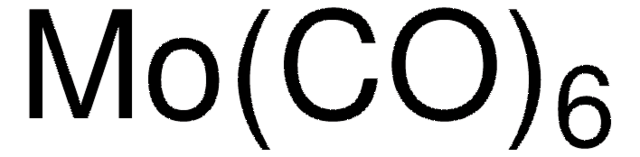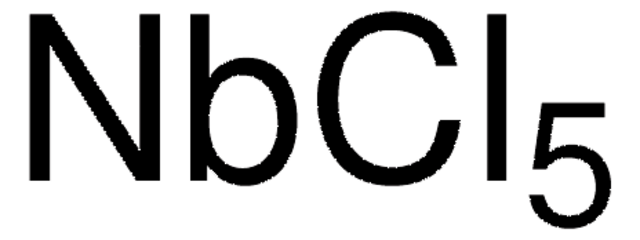642452
Molybdenum(V) chloride
anhydrous, powder, 99.99% trace metals basis (excluding W)
Synonyme(s) :
Molybdenum pentachloride, Molybdenum(5+) chloride
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Qualité
anhydrous
Niveau de qualité
Pression de vapeur
1.75 mmHg ( 25 °C)
131 mmHg ( 250 °C)
Essai
99.99% trace metals basis (excluding W)
Forme
powder
Impuretés
≤150.0 ppm Trace Metal Analysis
pb
268 °C (lit.)
Pf
194 °C (lit.)
Densité
2.928 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
Application(s)
battery manufacturing
Chaîne SMILES
Cl[Mo](Cl)(Cl)(Cl)Cl
InChI
1S/5ClH.Mo/h5*1H;/q;;;;;+5/p-5
Clé InChI
GICWIDZXWJGTCI-UHFFFAOYSA-I
Vous recherchez des produits similaires ? Visite Guide de comparaison des produits
Catégories apparentées
Description générale
Application
- As a catalyst for amidation of secondary benzyl alcohols.
- As a precursor to fabricate MoS2 thin films by atomic layer deposition method.
- As a primary catalyst for coordination polymerization of butadiene.
- To fabricate superior anode materials for Na-ion and Li-ion batteries.
- As a dual-function redox mediator for Li–O2 batteries to overcome thehigh polarization and low energy density issues.
À utiliser avec
Mention d'avertissement
Danger
Mentions de danger
Conseils de prudence
Classification des risques
Skin Corr. 1B
Code de la classe de stockage
8A - Combustible corrosive hazardous materials
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 3
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Équipement de protection individuelle
Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves, type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Articles
Advances in materials have often been led by the development of new synthetic methods that provide control over size, morphology and structure.
Advances in materials have often been led by the development of new synthetic methods that provide control over size, morphology and structure. The preparation of materials in a scalable and continuous manner is critical when development moves beyond lab-scale quantities.
We presents an article about a micro review of reversible addition/fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization. RAFT (Reversible Addition/Fragmentation Chain Transfer) polymerization is a reversible deactivation radical polymerization (RDRP) and one of the more versatile methods for providing living characteristics to radical polymerization.
Tools for Performing ATRP
Protocoles
We present an article about RAFT, or Reversible Addition/Fragmentation Chain Transfer, which is a form of living radical polymerization.
We presents an article featuring procedures that describe polymerization of methyl methacrylate and vinyl acetate homopolymers and a block copolymer as performed by researchers at CSIRO.
An article about the typical procedures for polymerizing via ATRP, which demonstrates that in the following two procedures describe two ATRP polymerization reactions as performed by Prof. Dave Hadddleton′s research group at the University of Warwick.
Contenu apparenté
We offer a complete line of the highest purity inorganic salts and materials for the micro and nanoelectronics market.
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique