Y0503
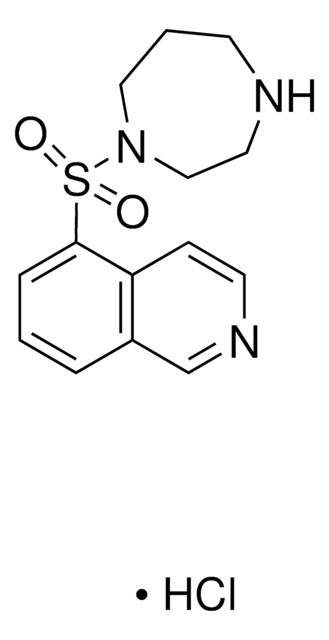
Y-27632 dihydrochloride
≥98% (HPLC)
Synonym(s):
Rock inhibitor y-27632, Y-27632 2HCl, (R)-(+)-trans-4-(1-Aminoethyl)-N-(4-Pyridyl)cyclohexanecarboxamide dihydrochloride
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
synthetic (organic)
Quality Level
Assay
≥98% (HPLC)
form
powder
optical activity
[α]/D +3.0 to +5.0°, c = 1.0 in methanol
color
white to beige
solubility
H2O: 14 mg/mL
storage temp.
2-8°C
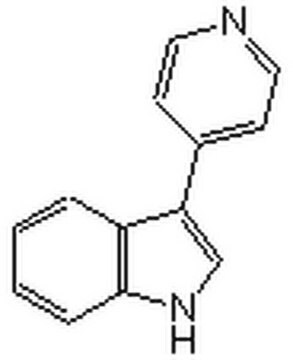
SMILES string
Cl.Cl.C[C@@H](N)[C@H]1CC[C@@H](CC1)C(=O)Nc2ccncc2
InChI
1S/C14H21N3O.2ClH/c1-10(15)11-2-4-12(5-3-11)14(18)17-13-6-8-16-9-7-13;;/h6-12H,2-5,15H2,1H3,(H,16,17,18);2*1H/t10-,11-,12-;;/m1../s1
InChI key
IDDDVXIUIXWAGJ-LJDSMOQUSA-N
Gene Information
human ... ROCK1(6093) , ROCK2(9475)
General description
Application
- as a medium supplement in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma organoid culture
- in the inhibition of Ras homolog gene family (Rho) kinase in mouse embryonic stem cells
- in the inhibition of Rho-associated protein kinase (ROCK) in human embryonic stem cells and human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs)
- Y-27632 dihydrochloride has been used as a supplement in the E8 medium to promote in vitro differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells
Biochem/physiol Actions
Features and Benefits
Legal Information
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Naive pluripotent stem cells are located within the epiblast of mature blastocysts. These primitive “ground-state” cells may be cultured in vitro using specialized media and small molecule inhibitors.
Organoid culture products to generate tissue and stem cell derived 3D brain, intestinal, gut, lung and cancer tumor organoid models.
Related Content
Discover Bioactive Small Molecules for Kinase Phosphatase Biology
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service




![[Leu15]-Gastrin I human ≥95% (HPLC)](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/153/342/d4cb3dd7-13f1-46cf-8d1f-3907a5de7a83/640/d4cb3dd7-13f1-46cf-8d1f-3907a5de7a83.png)