SRP6310
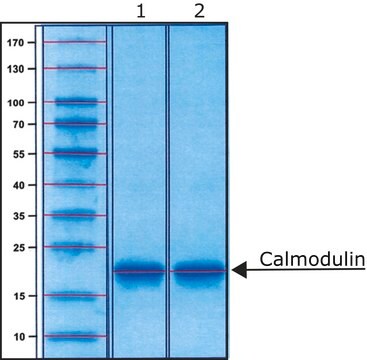
Calmodulin from bovine brain
≥95% (SDS-PAGE)
Sinónimos:
CALM, CAM
Iniciar sesiónpara Ver la Fijación de precios por contrato y de la organización
About This Item
Código UNSPSC:
12352200
NACRES:
NA.32
Productos recomendados
origen biológico
bovine brain
Análisis
≥95% (SDS-PAGE)
formulario
lyophilized
mol peso
16 kDa
envase
pkg of 1 mg
pkg of 500 μg
idoneidad
suitable for chromatography
Nº de acceso UniProt
Condiciones de envío
wet ice
temp. de almacenamiento
−20°C
Información sobre el gen
bovine ... CAM(520277)
Descripción general
Calmodulin (CaM) is a ubiquitous, calcium-binding protein. CaM is expressed in many cell types and can have different subcellular locations, including the cytoplasm, within organelles, or associated with the plasma or organelle membranes. Many of the proteins that CaM binds are unable to bind calcium themselves, and as such use CaM as a calcium sensor and signal transducer. CaM can also make use of the calcium stores in the endoplasmic reticulum, and the sarcoplasmic reticulum. CaM undergoes a conformational change upon binding to calcium, which enables it to bind to specific proteins for a specific response.
Aplicación
Calmodulin from bovine brain has been used to study calmodulin-associated endothelium-derived relaxing factor/nitric oxide synthase activity in the particulate and cytosolic fractions of bovine aortic endothelial cells. It has also been used as a standard in size-exclusion chromatography.
Acciones bioquímicas o fisiológicas
Calmodulin (CaM) can bind to and regulate a multitude of different protein targets, thereby affecting many different cellular functions. It is involved in inflammation, metabolism, apoptosis, muscle contraction, intracellular movement, short-term and long-term memory, nerve growth and the immune response. CaM can bind up to four calcium ions, and can undergo post-translational modifications, such as phosphorylation, acetylation, methylation and proteolytic cleavage, each of which can potentially modulate its actions.
Forma física
Lyophilized in 30 mM Hepes, pH 7.4, 1 mM CaCl2 and 0.1 mM DTT.
Reconstitución
In water or aqueous buffer
Palabra de señalización
Warning
Frases de peligro
Consejos de prudencia
Clasificaciones de peligro
Eye Irrit. 2
Código de clase de almacenamiento
11 - Combustible Solids
Clase de riesgo para el agua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto de inflamabilidad (°F)
Not applicable
Punto de inflamabilidad (°C)
Not applicable
Certificados de análisis (COA)
Busque Certificados de análisis (COA) introduciendo el número de lote del producto. Los números de lote se encuentran en la etiqueta del producto después de las palabras «Lot» o «Batch»
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Intestinal calmodulin and calcium-binding protein differ in their distribution and in the effect of vitamin D steroids on their concentration.
Thomasset M, et al.
Febs Letters, 127, 13-16 (1981)
Teaching Molecular Biology using computational tools and tacking into account the learning styles of students.
Craciun D and Isvoran A
Romanian Biotechnological Letters, 14.4, 4567-4574 (2009)
Calmodulin methyltransferase is an evolutionarily conserved enzyme that trimethylates Lys-115 in calmodulin.
Magnani R, et al.
Nature Communications, 43, doi: 10-doi: 10 (2010)
Calmodulin is a subunit of nitric oxide synthase from macrophages.
Cho HJ, et al.
The Journal of Experimental Medicine, 176, 599-604 (1992)
Ca2+ binding and conformational change in two series of point mutations to the individual Ca(2+)-binding sites of calmodulin.
Maune JF, et al.
The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 267, 5286-5295 (1992)
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico