SRP0120
Sirtuin 6 human
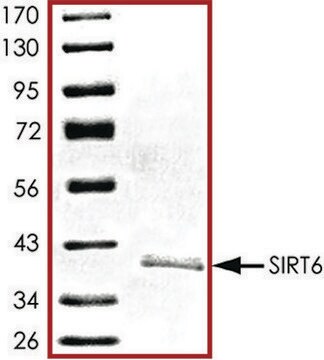
recombinant, expressed in E. coli, ≥70% (SDS-PAGE)
Sinónimos:
NAD-dependent ADP-ribosyltransferase sirtuin-6, SIR2L6, SIRT6, sir2-like 6
Iniciar sesiónpara Ver la Fijación de precios por contrato y de la organización
About This Item
Código UNSPSC:
12352200
NACRES:
NA.32
Productos recomendados
origen biológico
human
recombinante
expressed in E. coli
Ensayo
≥70% (SDS-PAGE)
Formulario
aqueous solution
mol peso
65 kDa
envase
pkg of 100 μg
condiciones de almacenamiento
avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles
concentración
>0.02 mg/mL
Nº de acceso NCBI
Nº de acceso UniProt
Condiciones de envío
dry ice
temp. de almacenamiento
−70°C
Información sobre el gen
human ... SIRT6(51548)
Descripción general
Sirtuin 6 (Sir6) is encoded by the gene mapped to human chromosome 19p13.3, a region linked with development of acute leukemia. Sir 6 is mainly expressed in bone cells and in the ovaries, but it is absent in the bone marrow. Sirt6 is a chromatin-associated protein localized specifically in nucleus.
Human Sirtuin 6, GenBank Accession No. NM_016539), full length with N-terminal ST tag, MW = 65kDa, expressed in Escherichia coli expression system.
Human Sirtuin 6, GenBank Accession No. NM_016539), full length with N-terminal ST tag, MW = 65kDa, expressed in Escherichia coli expression system.
Aplicación
Useful for the study of enzyme kinetics, screening inhibitors, and selectivity profiling.
Acciones bioquímicas o fisiológicas
Sirtuin 6 (Sir6) is a mono-ADP-ribosyltransferase, which catalyzes the transfer of ADP-ribose moiety from NAD to itself and histones. It has been implicated in the regulation of DNA repair, genomic stability and telomere integrity, gene expression, and metabolism. In addition, it also prevents age-related disorders and premature aging. Sir6 plays a vital role in the inhibition of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB)–mediated inflammatory responses in rheumatoid joints. Hence, Sir6 is considered to be a potent target for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Sir6 is also majorly implicated in the regulation of glucose and fat metabolism. Sir6 prevent cardiac hypertrophy in vitro via inhibiting NF-κB-dependent transcriptional activity and this effect is relied on its deacetylase activity.
Forma física
Formulated in 25 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0, 100 mM NaCl, 0.05% Tween-20 and 20% glycerol.
Nota de preparación
Thaw on ice. Upon first thaw, briefly spin tube containing enzyme to recover full content of the tube. Aliquot enzyme into single use aliquots. Store remaining undiluted enzyme in aliquots at -70°C. Note: Enzyme is very sensitive to freeze/thaw cycles.
Elija entre una de las versiones más recientes:
Certificados de análisis (COA)
Lot/Batch Number
¿No ve la versión correcta?
Si necesita una versión concreta, puede buscar un certificado específico por el número de lote.
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Abhishek Bhardwaj et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 113(5), E538-E547 (2016-01-21)
SIRT6 (sirtuin 6) is a member of sirtuin family of deacetylases involved in diverse processes including genome stability, metabolic homeostasis, and tumorigenesis. However, the role of SIRT6 deacetylase activity in its tumor-suppressor functions is not well understood. Here we report
Neural sirtuin 6 (Sirt6) ablation attenuates somatic growth and causes obesity.
Schwer B
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA, 107(50), 21790-21794 (2010)
Chromosomal organization and fluorescence in situ hybridization of the human Sirtuin 6 gene.
Mahlknecht U
International Journal of Oncology, 28(2), 447-456 (2006)
Minna Rahnasto-Rilla et al.
Chembiochem : a European journal of chemical biology, 17(1), 77-81 (2015-11-27)
Sirtuin 6 (SIRT6) is an NAD+-dependent histone deacetylase enzyme that is involved in multiple molecular pathways related to aging. Initially, it was reported that SIRT6 selectively deacetylated H3K9Ac and H3K56Ac; however, it has more recently been shown to preferentially hydrolyze long-chain
Overexpression of sirtuin 6 suppresses inflammatory responses and bone destruction in mice with collagen-induced arthritis.
Lee HS
Arthritis and Rheumatism, 65(7), 1776-1785 (2013)
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico


![[Tyr(SO3H)63]-Hirudin Fragment 54-65 ≥95% (HPLC)](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/401/056/a0ac1972-7f9e-45b9-8e32-74f3f275e097/640/a0ac1972-7f9e-45b9-8e32-74f3f275e097.png)
