P3243
Phosphodiesterase I from Crotalus adamanteus venom
vial of ≥100 units, Purified
Sinónimos:
5′-Exonuclease, Oligonucleate 5′-nucleotidohydrolase
Iniciar sesiónpara Ver la Fijación de precios por contrato y de la organización
About This Item
Productos recomendados
origen biológico
Crotalus adamanteus venom
Nivel de calidad
Formulario
solid
calidad
Purified
actividad específica
≥20.0 unit/mg solid
envase
vial of ≥100 units
temp. de almacenamiento
−20°C
¿Está buscando productos similares? Visita Guía de comparación de productos
Aplicación
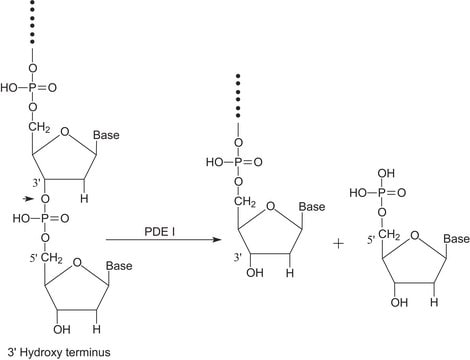
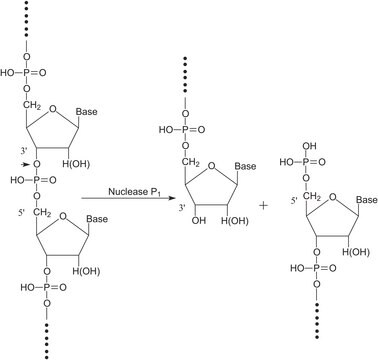
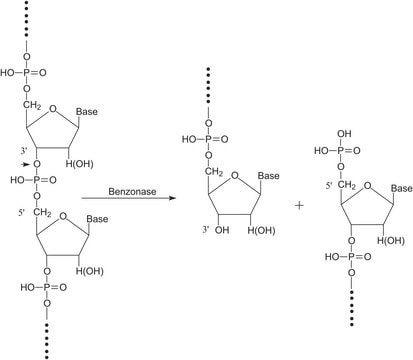
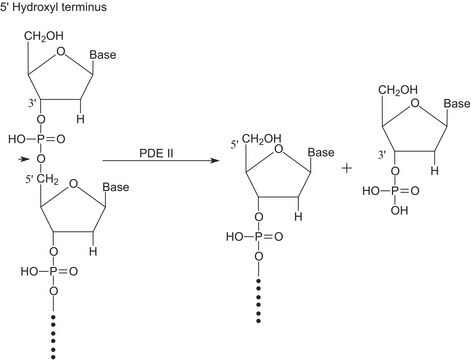
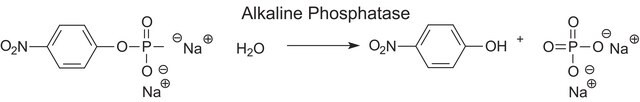
Phosphodiesterase (PDE) is any enzyme that is used to breaks phosphodiester bonds. It is a membrane-bound glycoprotein that is used to catalyze the hydrolysis of various nucleotide polyphosphates. Phosphodiesterase I is used in phosphodiesterase activation assays to hydrolyze AMP. Product P3243 is from Crotalus adamanteus venom and is purified. Product P3243 has been used to hydrolyze tRNA with wyosine derivatives into mononucleosides.
Acciones bioquímicas o fisiológicas
Phosphodiesterase I breaks phosphodiester bonds and catalyzes the hydrolysis of various nucleotide polyphosphates. Phosphodiesterase I is released from eucaryotic plasma membranes by phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C.
Definición de unidad
One Unit hydrolyzes one μmole of p-nitrophenyl thymidine-5-phosphate per minute at 25 °C, pH 8.9
Nota de preparación
Purified via the method of Williams, et al. and further treated to inactivate contaminating 5′-nucleotidase activity.
Reconstitución
For testing purposes, PDE I is reconstituted in cold deionized water at 0.1 - 0,2 un/mL.
Palabra de señalización
Danger
Frases de peligro
Consejos de prudencia
Clasificaciones de peligro
Resp. Sens. 1
Código de clase de almacenamiento
13 - Non Combustible Solids
Clase de riesgo para el agua (WGK)
WGK 1
Punto de inflamabilidad (°F)
Not applicable
Punto de inflamabilidad (°C)
Not applicable
Elija entre una de las versiones más recientes:
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Action of venom phosphodiesterase on deoxyribonucleic acid.
E J WILLIAMS et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 236, 1130-1134 (1961-04-01)
Valérie de Crécy-Lagard et al.
Molecular biology and evolution, 27(9), 2062-2077 (2010-04-13)
Wyosine (imG) and its derivatives such as wybutosine (yW) are found at position 37 of phenylalanine-specific transfer RNA (tRNA(Phe)), 3' adjacent to the anticodon in Eucarya and Archaea. In Saccharomyces cerevisiae, formation of yW requires five enzymes acting in a
Alain R Weber et al.
Nature communications, 7, 10806-10806 (2016-03-05)
Cytosine methylation in CpG dinucleotides is an epigenetic DNA modification dynamically established and maintained by DNA methyltransferases and demethylases. Molecular mechanisms of active DNA demethylation began to surface only recently with the discovery of the 5-methylcytosine (5mC)-directed hydroxylase and base
N Shenoy et al.
Blood cancer journal, 7(7), e587-e587 (2017-07-22)
The Ten Eleven Translocation (TET) enzymes have been found to be mutated in both diffuse large B-cell (DLBCL) and peripheral T-cell (PTCL) lymphomas resulting in DNA hypermethylation. Recent studies in embryonal stem cells showed that ascorbic acid (AA) is a
Yana Konokhova et al.
Skeletal muscle, 6, 10-10 (2016-02-20)
Low mitochondrial content and oxidative capacity are well-established features of locomotor muscle dysfunction, a prevalent and debilitating systemic occurrence in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Although the exact cause is not firmly established, physical inactivity and oxidative stress
Protocolos
Enzymatic Assay of 5’-Nucleotidase
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico