F2733
Human Fibronectin
from human plasma, liquid, FITC labeled, suitable for cell culture
Sinónimos:
Fibronectin
About This Item
Productos recomendados
Nombre del producto
Fibronectin-FITC, FITC-labeled human plasma fibronectin, Suitable for cell culture
origen biológico
human
Nivel de calidad
Formulario
liquid
condiciones de almacenamiento
protect from light
dilution
(invadopodia invasion assay: suitable)
Condiciones de envío
dry ice
temp. de almacenamiento
−20°C
Descripción general
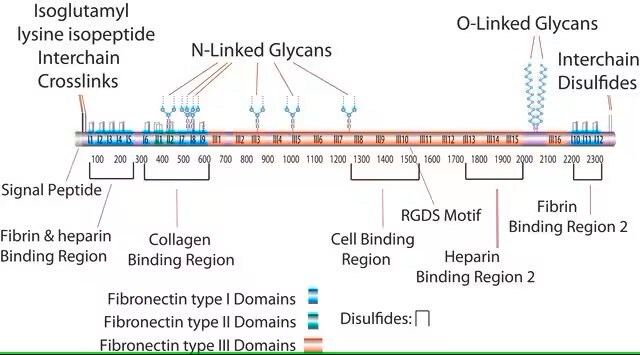
Fibronectin, also known as Cold-insoluble globulin, is a large glycoprotein of the extracellular matrix that is coded by FN1 gene. It is expressed in the plasma and at the cell surface. Fibronectin is a ubiquitous and essential component of the extracellular matrix (ECM) and plays a vital role during tissue repair. Fibronectin functions both as a regulator of cellular processes and an important scaffolding protein to maintain and direct tissue organization and ECM composition. Fibronectin plays an important role in cell adhesion and spreading and affect the routes of cell migration both in vivo and in culture.
Proteolytic degradation of extracellular matrix (ECM) is a critical step during cell invasion and tissue transmigration that is required for many physiological and pathological processes. Cellular structures that mediate cell adhesion to, degradation of, and invasion into ECM are invadopodia of transformed and tumor cells and podosomes of osteoclasts, macrophages, normal monocytic, endothelial, and smooth muscle cells. The ability to degrade extracellular matrix (ECM) is a hallmark of invasive tumors and is thought to be essential for the movement of cancer cells through tissue barriers.
The invadopodia assay is method that has been most informative for pinpointing regions of the cell that initiate invasion involve plating cells on a culture surface coated with a thin layer of fluorescently labeled matrix, and visualizing regions where the cell has degraded the matrix to create an area devoid of fluorescence.The assay have revealed that invasive cells extend small localized protrusions that degrade the matrix. This invadopodia invasion assay may be used for assessing activity of different cell types as well as individual cells in heterogeneous populations may be analyzed for invasive potential. The number and invadopodia activity are sensitive to some physical or chemical factors such as: cell type, matrix rigidity, density of cell layer.
Código de clase de almacenamiento
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
Clase de riesgo para el agua (WGK)
WGK 1
Elija entre una de las versiones más recientes:
Certificados de análisis (COA)
It looks like we've run into a problem, but you can still download Certificates of Analysis from our Documentos section.
Si necesita más asistencia, póngase en contacto con Atención al cliente
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico