E2412
Pullulanase microbial
Sinónimos:
Pullulanase microbial, Promozyme® D2
Iniciar sesiónpara Ver la Fijación de precios por contrato y de la organización
About This Item
Número de CAS:
Número MDL:
Código UNSPSC:
12352204
NACRES:
NA.54
Productos recomendados
recombinante
expressed in Bacillus subtilis
Formulario
aqueous solution
actividad específica
≥1000 NPUN/g
temp. de almacenamiento
2-8°C
Aplicación
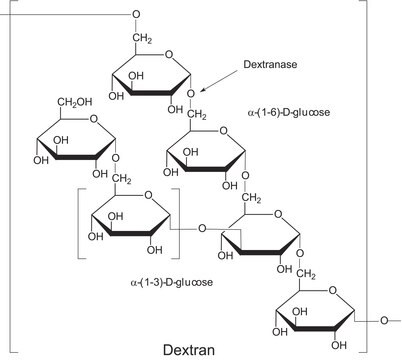
Pullulanase is a glucanase that degrades pullulan. It is commonly used for starch-debranching as well as to study polysaccharide utilization.
Acciones bioquímicas o fisiológicas
Type I pullulanases specifically hydrolyse α-1,6 linkages, while type II pullulanases are also able to hydrolyse α-1,4 linkages.
Otras notas
View more information on enzymes for complex carbohydrate analysis at www.sigma-aldrich.com/enzymeexplorer
Información legal
A product of Novozymes Corp.
Novozym is a registered trademark of Novozymes A/S
Promozyme is a trademark of Novozymes Corp.
Código de clase de almacenamiento
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
Clase de riesgo para el agua (WGK)
WGK 1
Punto de inflamabilidad (°F)
Not applicable
Punto de inflamabilidad (°C)
Not applicable
Elija entre una de las versiones más recientes:
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Los clientes también vieron
K A Smith et al.
Journal of bacteriology, 171(4), 2116-2123 (1989-04-01)
We have cloned a pullulanase gene from Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron. The pullulanase expressed from this clone in Escherichia coli was cell associated and soluble and had a molecular mass of 72 kilodaltons by gel filtration. Maxicell analysis of proteins coded by
Nasima Chorfa et al.
Polymers, 14(10) (2022-05-29)
In this work, a valorization of the starch stemming from downgraded potatoes was approached through the preparation of starch nanoparticles using different physical methods, namely liquid and supercritical carbon dioxide, high energy ball milling (HEBM), and ultrasonication on the one
Christopher C Ibenegbu et al.
Microbial cell factories, 21(1), 251-251 (2022-11-30)
The starch in waste bread (WB) from industrial sandwich production was directly converted to ethanol by an amylolytic, ethanologenic thermophile (Parageobacillus thermoglucosidasius strain TM333) under 5 different simultaneous saccharification and fermentation (SSF) regimes. Crude α-amylase from TM333 was used alone
Kornelia T Kaczmarska et al.
Journal of agricultural and food chemistry, 65(46), 10064-10073 (2017-10-24)
This study investigated the effect of germination and fermentation on the composition of carbohydrates in Australian sweet lupin. Specifically, the amount of sugars (sucrose, fructose, and glucose), starch, oligosaccharides (verbascose, stachyose, and raffinose), and dietary fiber were measured in germinated
Youran Li et al.
Journal of agricultural and food chemistry, 60(44), 11164-11172 (2012-10-18)
The pulA1 gene, encoding a novel thermostable type I pullulanase PulA1 from Bacillus sp. CICIM 263, was identified from genomic DNA. The open reading frame of the pulA1 gene was 2655 base pairs long and encoded a polypeptide (PulA1) of
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico