A5691
Anti-actina, α-músculo liso monoclonal
clone 1A4, purified from hybridoma cell culture
Sinónimos:
SMA
About This Item
Productos recomendados
origen biológico
mouse
Nivel de calidad
conjugado
alkaline phosphatase conjugate
forma del anticuerpo
purified from hybridoma cell culture
tipo de anticuerpo
primary antibodies
clon
1A4, monoclonal
formulario
buffered aqueous glycerol solution
mol peso
antigen ~42 kDa
reactividad de especies
human, mouse, rat, chicken, frog, canine, rabbit, guinea pig, goat, bovine, sheep, snake
técnicas
ELISA: suitable
immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded sections): 1:20 using human tonsil or appendix sections
western blot: 1:100 using chicken gizzard extract/ Mouse heart extract
isotipo
IgG2a
Nº de acceso UniProt
Condiciones de envío
wet ice
temp. de almacenamiento
2-8°C
modificación del objetivo postraduccional
unmodified
Información sobre el gen
mouse ... Acta2(11475)
rat ... Acta2(81633)
¿Está buscando productos similares? Visita Guía de comparación de productos
Descripción general
Inmunógeno
Aplicación
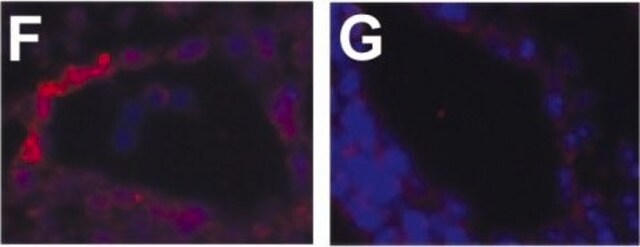
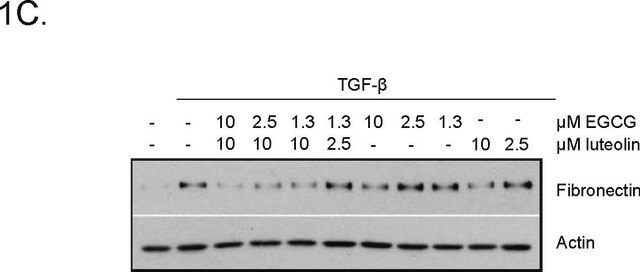
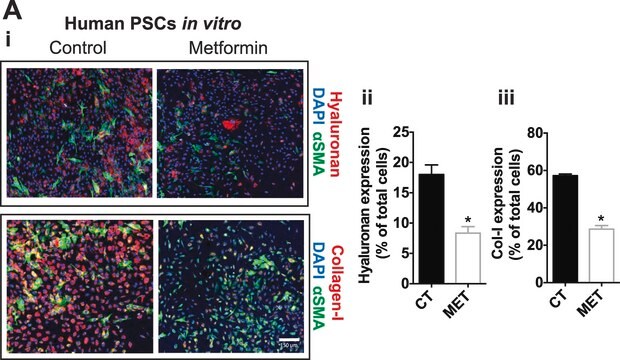
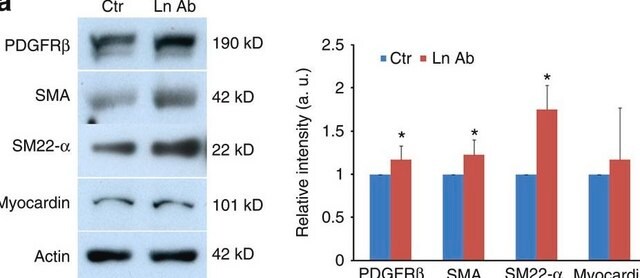
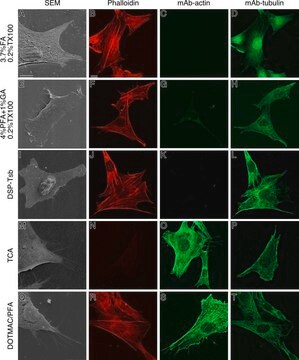
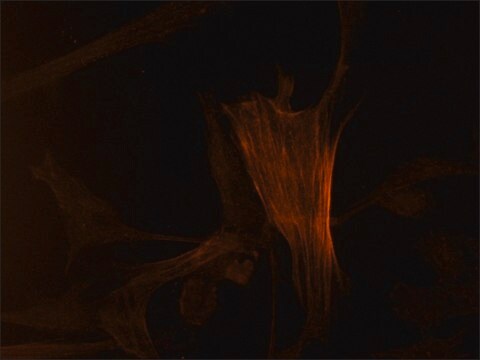
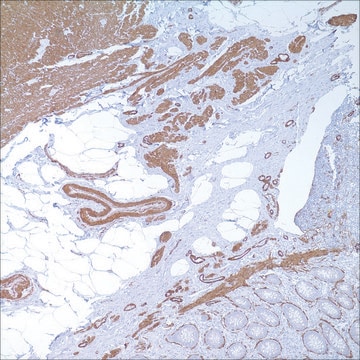
Se realizó análisis mediante IHC de tejido cardiaco de ratón teñido con x-gal utilizando el anticuerpo monoclonal primario anti-actina de músculo liso de ratón para identificar los miofibroblastos.
Immunohistochemistry (1 paper)
Forma física
Otras notas
Cláusula de descargo de responsabilidad
¿No encuentra el producto adecuado?
Pruebe nuestro Herramienta de selección de productos.
Código de clase de almacenamiento
10 - Combustible liquids
Clase de riesgo para el agua (WGK)
WGK 2
Equipo de protección personal
Eyeshields, Gloves, multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US)
Certificados de análisis (COA)
Busque Certificados de análisis (COA) introduciendo el número de lote del producto. Los números de lote se encuentran en la etiqueta del producto después de las palabras «Lot» o «Batch»
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Los clientes también vieron
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico