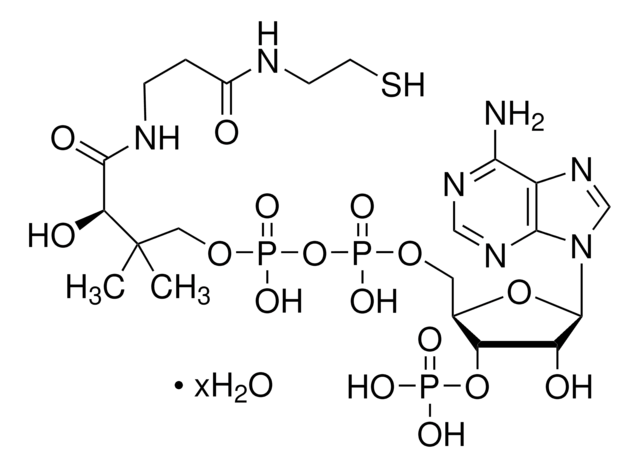
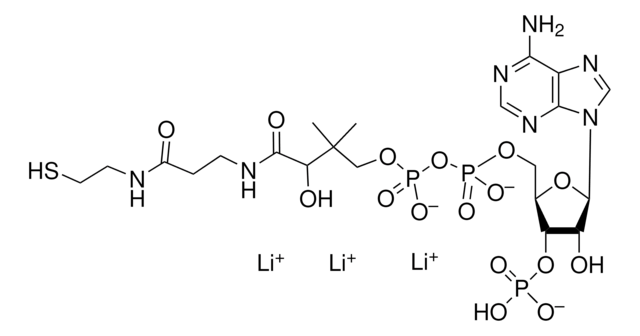
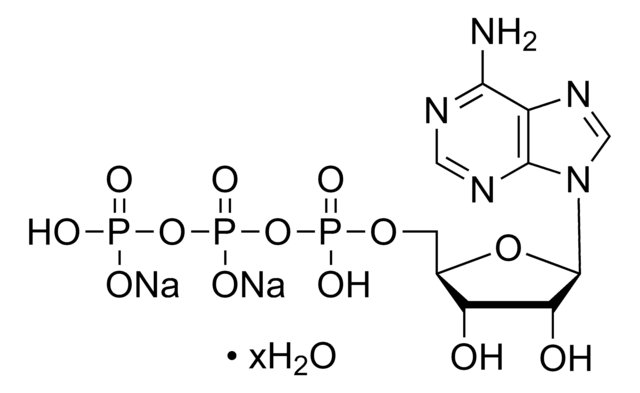
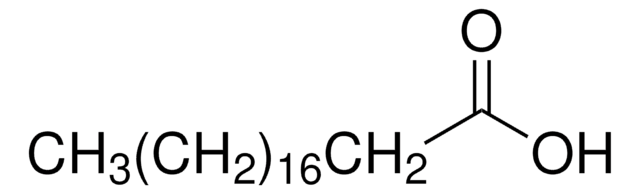A3352
Acyl-coenzyme A Synthetase from Pseudomonas sp.
≥2 units/mg protein
Sinónimos:
Acid: CoA ligase (AMP-forming)
Iniciar sesiónpara Ver la Fijación de precios por contrato y de la organización
About This Item
Productos recomendados
Formulario
powder
Nivel de calidad
actividad específica
≥2 units/mg protein
Condiciones de envío
dry ice
temp. de almacenamiento
−20°C
¿Está buscando productos similares? Visita Guía de comparación de productos
Descripción general
Acyl-coenzyme A synthetase belongs to adenylate-forming enzymes superfamily. It has a conserved adenosine triphosphate/adenosine monophosphate (ATP/AMP) binding motif.
Aplicación
Acyl-coenzyme A (coA) synthetase from Pseudomonas sp. has been used:
- as ligase in the synthesis of mevalonate derivatives of adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
- in in vitro fatty acylation assays
- in the synthesis of (14C)Vernoloyl-CoA (Va-CoA),(3) bisphosphonates derivatives of ATP(4) and (3H)Palmitate-CoA
Acyl-coenzyme A Synthetase may be used to study fatty acid metabolism and lipid metabolism. It has been used to study its interaction with fatty acid transport proteins, which has been found to be involved in the efficient cellular uptake of long-chain fatty acids in adipocytes .
Acciones bioquímicas o fisiológicas
Acyl coenzyme A synthetase proteins are involved in regulating and facilitating long-chain fatty acid transport in mammalian cells .
Acyl-coenzyme A (CoA) synthetase (ACS) enzyme catalyzes a two-step thioesterification reaction involving the conversion of free fatty acids (FAs) to CoA esters. The substrate for ACS varies from two carbon to 26 carbon FAs. It is involved in the activation of FAs for lipid metabolism and enables FA to participate in various cellular metabolic pathways.
Definición de unidad
One unit will form 1.0 μmole of AMP and oleoyl coenzyme A from ATP and oleate at pH 8.1 at 25 °C in the presence of Coenzyme A.
Código de clase de almacenamiento
11 - Combustible Solids
Clase de riesgo para el agua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto de inflamabilidad (°F)
Not applicable
Punto de inflamabilidad (°C)
Not applicable
Equipo de protección personal
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Elija entre una de las versiones más recientes:
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Los clientes también vieron
Structural snapshots for the conformation-dependent catalysis by human medium-chain acyl-coenzyme A synthetase ACSM2A
Kochan G, et al.
Journal of Molecular Biology, 388(5), 997-1008 (2009)
Synthesis of ATP derivatives of compounds of the mevalonate pathway (isopentenyl di-and triphosphate; geranyl di-and triphosphate, farnesyl di-and triphosphate, and dimethylallyl diphosphate) catalyzed by T4 RNA ligase, T4 DNA ligase and other ligases: Potential relationship with the effect of bisphosphonates on osteoclasts
Sillero MAG, et al.
Biochemical Pharmacology, 78(4), 335-343 (2009)
Naohiro Kurotaki et al.
PloS one, 6(5), e20589-e20589 (2011-06-10)
The recent development of high-resolution DNA microarrays, in which hundreds of thousands of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) are genotyped, enables the rapid identification of susceptibility genes for complex diseases. Clusters of these SNPs may show runs of homozygosity (ROHs) that
A Ruść et al.
Meat science, 89(4), 440-443 (2011-06-10)
The aim of the study was to check whether different genotypes at acyl-CoA synthetase (ACSL4 locus, SNP G2645A) are associated with pork quality. 132 (Landrace × Yorkshire) × Duroc fatteners were genotyped by originally developed PCR-RFLP method. Upon the slaughter
Michael Veit et al.
Methods in molecular biology (Clifton, N.J.), 446, 163-182 (2008-04-01)
Palmitoylation or S-acylation is the post-translational attachment of fatty acids to cysteine residues and is common among integral and peripheral mem brane proteins. Palmitoylated proteins have been found in every eukaryotic cell type examined (yeast, insect, and vertebrate cells), as
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico