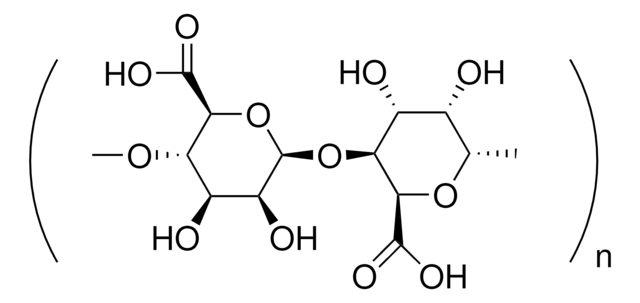
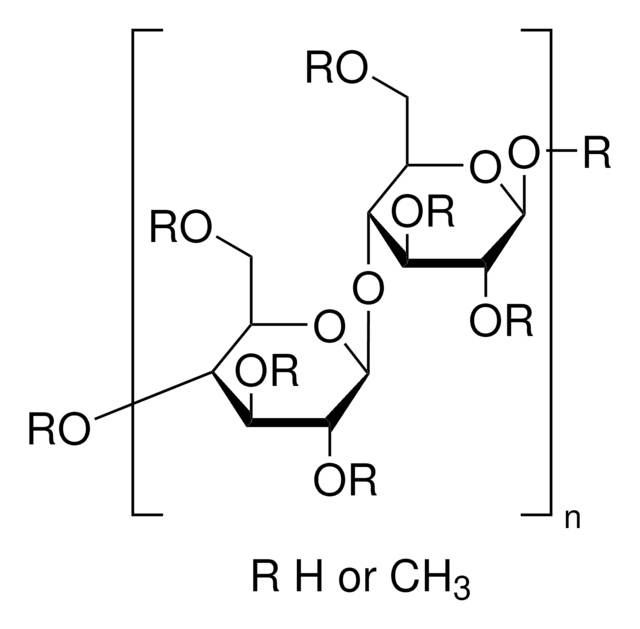
A2033
Ácido algínico sodium salt from brown algae
Medium viscosity
Sinónimos:
Algin, Alginato de sodio
About This Item
Productos recomendados
origen biológico
algae (brown)
Nivel de calidad
formulario
powder
color
white to brown
viscosidad
≥2,000 cP, 2 %(25 °C)
solubilidad
water: 10 mg/mL, slightly hazy to strongly hazy, faintly yellow to yellow
temp. de almacenamiento
2-8°C
InChI
1S/C6H10O7.Na/c7-1-2(8)4(5(10)11)13-6(12)3(1)9;/h1-4,6-9,12H,(H,10,11);/q;+1/p-1/t1-,2-,3-,4?,6+;/m0./s1
Clave InChI
MSXHSNHNTORCAW-MPGIDXPLSA-M
¿Está buscando productos similares? Visita Guía de comparación de productos
Aplicación
Otras notas
Código de clase de almacenamiento
11 - Combustible Solids
Clase de riesgo para el agua (WGK)
WGK 1
Punto de inflamabilidad (°F)
Not applicable
Punto de inflamabilidad (°C)
Not applicable
Equipo de protección personal
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Certificados de análisis (COA)
Busque Certificados de análisis (COA) introduciendo el número de lote del producto. Los números de lote se encuentran en la etiqueta del producto después de las palabras «Lot» o «Batch»
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico