11767291910
Roche
TUNEL Label Mix
sufficient for 30 tests, pkg of 3 × 550 μL
Sinónimos:
transferase dUTP nick end labeling, tunel
About This Item
Productos recomendados
Formulario
solution
Nivel de calidad
uso
sufficient for 30 tests
envase
pkg of 3 × 550 μL
fabricante / nombre comercial
Roche
color
colorless
solubilidad
water: miscible
temp. de almacenamiento
−20°C
Categorías relacionadas
Descripción general
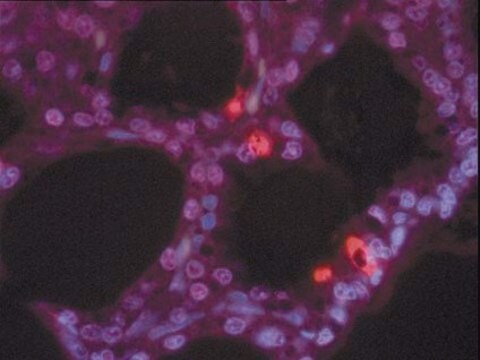
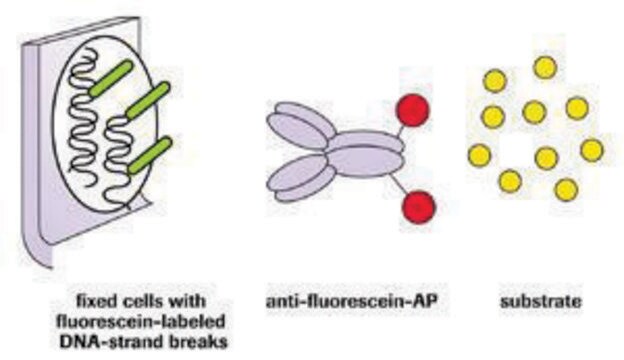
Aplicación
Nota de preparación
For one test: Mix 45 μl TUNEL Label with 5 μl TUNEL Enzyme prior to use. For negative control use 50 μl/test TUNEL Label only.
Storage conditions (working solution): Note: The TUNEL reaction mixture (45 μl TUNEL Label with 5 μl TUNEL Enzyme for 1 test) should be prepared just before use, and should not be stored. Keep the TUNEL reaction mixture on ice until use.
Otras notas
Palabra de señalización
Danger
Frases de peligro
Consejos de prudencia
Clasificaciones de peligro
Aquatic Chronic 2 - Carc. 1B Inhalation
Código de clase de almacenamiento
6.1D - Non-combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic hazardous materials or hazardous materials causing chronic effects
Clase de riesgo para el agua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto de inflamabilidad (°F)
does not flash
Punto de inflamabilidad (°C)
does not flash
Elija entre una de las versiones más recientes:
Certificados de análisis (COA)
It looks like we've run into a problem, but you can still download Certificates of Analysis from our Documentos section.
Si necesita más asistencia, póngase en contacto con Atención al cliente
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Los clientes también vieron
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico