11427598910
Roche
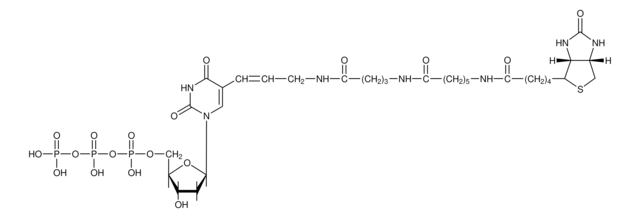
Biotin-16-ddUTP
≥98% (HPLC), solution, 1 mM, suitable for hybridization
Sinónimos:
Bio-16-ddUTP tetralithium salt, 5-(N-[N-Biotinyl-ε-aminocaproyl-γ-aminobutyryl]-3-aminoallyl)-2′,3′-dideoxyuridine 5′-triphosphate
Iniciar sesiónpara Ver la Fijación de precios por contrato y de la organización
About This Item
Fórmula empírica (notación de Hill):
C32H52N7O17P3S
Número de CAS:
Peso molecular:
931.78
Código UNSPSC:
41116100
Productos recomendados
Nivel de calidad
Ensayo
≥98% (HPLC)
Formulario
solution
mol peso
955.5 (biotin-16-ddUTP-Li4)
envase
pkg of 25 μL (25 nmol; 1mM)
fabricante / nombre comercial
Roche
concentración
1 mM
técnicas
hybridization: suitable
temp. de almacenamiento
−20°C
¿Está buscando productos similares? Visita Guía de comparación de productos
Categorías relacionadas
Descripción general
Biotin-16-ddUTP, tetralithium salt; 1mM
Aplicación
- Biotin-16-ddUTP is used as a substrate for: Terminal Transferase
- DNA polymerase I (Holoenzyme and Klenow fragment)
- T4 DNA polymerase
- Taq DNA polymerase and reverse transcriptase (e.g.,Transcriptor).
- The biotin-labeled oligonucleotide can be used as a hybridization probe for: DNA and RNA transfers
- Colony and plaque screening
- In situ hybridization
The labeled oligomer can be subsequently detected by ELISA using the Streptavidin-AP conjugate for nucleic acid detection.
Oligonucleotides are enzymatically labeled at their 3′ end with Terminal Transferase by incorporation of a single biotin-labeled dideoxyuridine- triphosphate (biotin-ddUTP).
It has been used in the biotinylation of in vitro transcribed tmRNA during surface plasmon resonance (SPR) technique. It has been used in the standard nick translation reaction for tumor DNA labelling during comparative genomic hybridization.
Características y beneficios
Biotin is bound to dideoxyuridine triphosphate via an amide linkage.
Calidad
Typical analysis: At least 85% Biotin-16-ddUTP (HPLC, area%).
Otras notas
For life science research only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Código de clase de almacenamiento
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
Clase de riesgo para el agua (WGK)
nwg
Punto de inflamabilidad (°F)
does not flash
Punto de inflamabilidad (°C)
does not flash
Elija entre una de las versiones más recientes:
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Takahiro Okada et al.
Bioscience, biotechnology, and biochemistry, 68(11), 2319-2325 (2004-11-27)
Escherichia coli ribosomal protein S1 is composed of six repeating homologous oligonucleotide/oligosaccharide-binding fold (OB folds). In trans-translation, S1 plays a role in delivering transfer-messenger RNA (tmRNA) to stalled ribosomes. The second OB fold of S1 was found to be protected
Highly polymorphic microsatellite markers for the short-snouted seahorse (Hippocampus hippocampus), including markers from a closely related species the long-snouted seahorse (Hippocampus guttulatus).
van de Vliet M S, et al.
Conservation genetics resources, 1(1), 93-93 (2009)
Peter Liebisch et al.
British journal of haematology, 122(2), 193-201 (2003-07-09)
Chromosomal abnormalities, such as 13q deletions, are emerging as important prognostic factors in multiple myeloma. Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) using specific DNA probes is the technique most widely used for the determination of genomic aberrations in this disease. The
Microarray-based method for detection of unknown genetic modifications.
Torstein T, et al.
BMC biotechnology, 7(1), 91-91 (2007)
Hadar Golan Berman et al.
International journal of molecular sciences, 22(11) (2021-06-03)
Cisplatin is a chemotherapy drug that kills cancer cells by damaging their DNA. In human cells, this damage is repaired primarily by nucleotide excision repair. While cisplatin is generally effective, many cancers exhibit initial or acquired resistance to it. Here
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico