03353583910
Roche
DIG Oligonucleotide Tailing Kit, 2nd generation
sufficient for 25 reactions (100 pmol oligonucleotide per assay; 1 ug of a 30-mer oligonucleotide)
About This Item
Productos recomendados
uso
sufficient for 25 reactions (100 pmol oligonucleotide per assay; 1 ug of a 30-mer oligonucleotide)
Nivel de calidad
fabricante / nombre comercial
Roche
condiciones de almacenamiento
avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles
características de los productos alternativos más sostenibles
Designing Safer Chemicals
Learn more about the Principles of Green Chemistry.
sustainability
Greener Alternative Product
categoría alternativa más sostenible
Descripción general
Aplicación
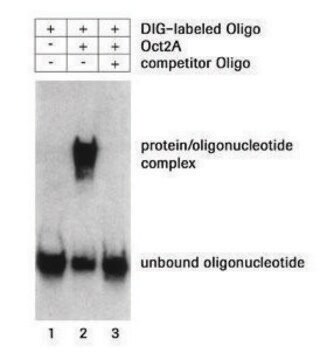
- northern blot assay
- in situ hybridization (ISH)
- fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH)
Características y beneficios
- Very sensitive hybridization probes, due to the incorporation of several DIG-nucleotides
- Fast hybridization kinetics, due to the small size of oligonucleotides
- Single-stranded probes, no renaturation during hybridization
- Sequence can be designed according to the experiment
- Specially suited for in situ hybridization; due to their small size, oligonucleotides readily diffuse into fixed tissues and cells
Envase
Principio
Nota de preparación
In one standard labeling reaction up to 100 pmol oligonucleotide (1 μg of a 30-mer oligonucleotide) can be applied.
Almacenamiento y estabilidad
Otras notas
Solo componentes del kit
- Reaction Buffer 5x concentrated
- CoCl<SUB>2</SUB> Solution 25 mM
- DIG-dUTP Solution 1 mM
- dATP Solution 10 mM
- Recombinant Terminal Transferase 400 U/μl
- Control Oligonucleotide, unlabeled 20 pmol/μl
- Oligonucleotide, DIG-dUTP/dATP tailed 2.5 pmol/μl
- Control DNA 0.25 mg/ml
- Glycogen Solution 20 mg/ml
- DNA Dilution Buffer, 50 μg/ml fish sperm DNA
- Poly(A) Solution 10 mg/ml
Palabra de señalización
Danger
Frases de peligro
Consejos de prudencia
Clasificaciones de peligro
Acute Tox. 4 Inhalation - Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Aquatic Chronic 2 - Carc. 1B Inhalation - Repr. 1B
Código de clase de almacenamiento
6.1D - Non-combustible, acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic hazardous materials or hazardous materials causing chronic effects
Clase de riesgo para el agua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto de inflamabilidad (°F)
does not flash
Punto de inflamabilidad (°C)
does not flash
Certificados de análisis (COA)
Busque Certificados de análisis (COA) introduciendo el número de lote del producto. Los números de lote se encuentran en la etiqueta del producto después de las palabras «Lot» o «Batch»
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Los clientes también vieron
Artículos
Digoxigenin (DIG) labeling methods and kits for DNA and RNA DIG probes, random primed DNA labeling, nick translation labeling, 5’ and 3’ oligonucleotide end-labeling.
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico