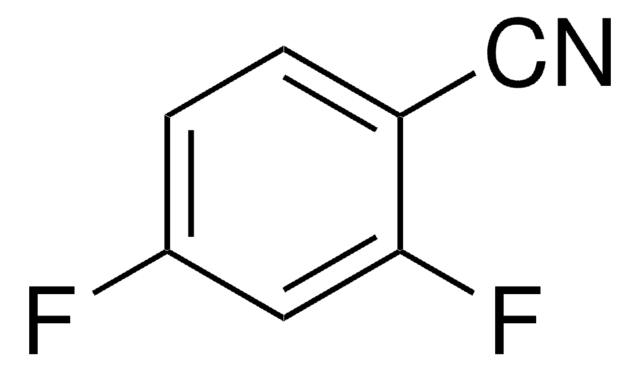
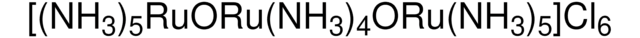D57558
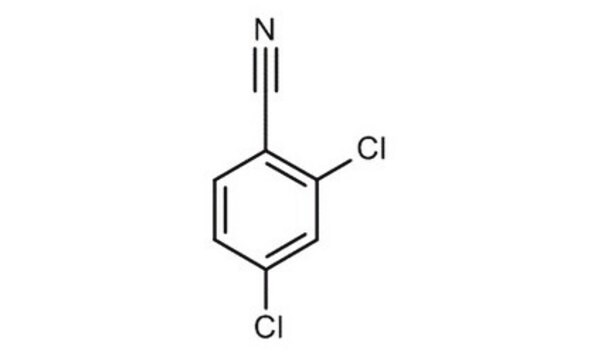
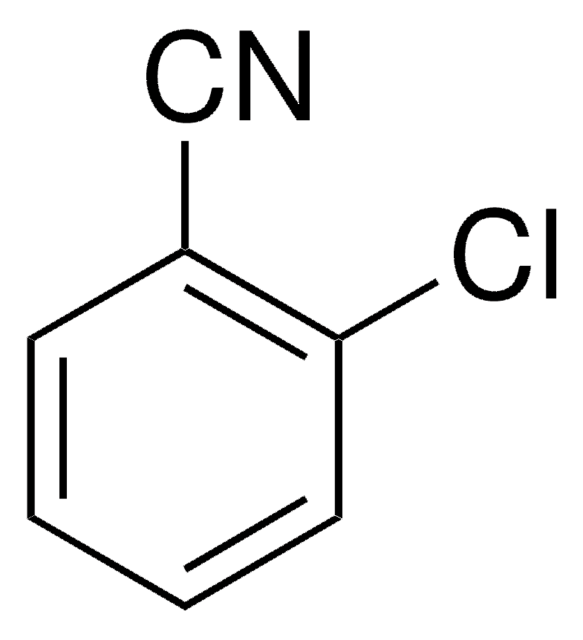
2,6-Dichlorobenzonitrile
97%
Sinónimos:
Dichlobenil
Iniciar sesiónpara Ver la Fijación de precios por contrato y de la organización
About This Item
Fórmula lineal:
Cl2C6H3CN
Número de CAS:
Peso molecular:
172.01
Beilstein:
1909167
Número CE:
Número MDL:
Código UNSPSC:
12352100
ID de la sustancia en PubChem:
NACRES:
NA.22
Productos recomendados
Análisis
97%
formulario
powder
mp
143-146 °C (lit.)
cadena SMILES
Clc1cccc(Cl)c1C#N
InChI
1S/C7H3Cl2N/c8-6-2-1-3-7(9)5(6)4-10/h1-3H
Clave InChI
YOYAIZYFCNQIRF-UHFFFAOYSA-N
¿Está buscando productos similares? Visita Guía de comparación de productos
Aplicación
2,6-Dichlorobenzonitrile can be used as a starting material to synthesize:
- 2,6-Dichlorobenzaldehyde using lithium N, N′-dimethylethylenediaminoaluminum hydride as a reducing agent.
- 5-(2,6-Dichlorophenyl)-2H-tetrazole via gold-catalyzed nucleophilic (3 + 2) cycloaddition reaction with sodium azide.
- 2,6-Dichlorobenzamide via hydrolysis using potassium tert-butoxide as a catalyst.
- Chloro-aminoindazole by reacting with hydrazine monohydrate.
- 2,6-Dichlorobenzenecarboselenoamide by treating with Woollins′ reagent.
Palabra de señalización
Warning
Frases de peligro
Consejos de prudencia
Clasificaciones de peligro
Acute Tox. 4 Dermal - Aquatic Chronic 2
Código de clase de almacenamiento
11 - Combustible Solids
Clase de riesgo para el agua (WGK)
WGK 2
Punto de inflamabilidad (°F)
Not applicable
Punto de inflamabilidad (°C)
Not applicable
Equipo de protección personal
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Elija entre una de las versiones más recientes:
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Los clientes también vieron
Synthesis of primary arylselenoamides by reaction of aryl nitriles with Woollins' reagent
Hua Guoxiong, et al.
Organic Letters, 8(23), 5251-5254 (2006)
Valeria Franceschini et al.
Stem cells (Dayton, Ohio), 27(4), 825-835 (2009-04-08)
The herbicide dichlobenil selectively causes necrosis of the dorsomedial part of olfactory neuroepithelium (NE) with permanent damage to the underlying mucosa, whereas the lateral part of the olfactory region and the nasal respiratory mucosa remain undamaged. We investigated here whether
L Peng et al.
Plant biology (Stuttgart, Germany), 15(2), 405-414 (2012-07-05)
Cellulose is the major component of plant cell walls and is an important source of industrial raw material. Although cellulose biosynthesis is one of the most important biochemical processes in plant biology, the regulatory mechanisms of cellulose synthesis are still
Fang Xie et al.
Toxicology and applied pharmacology, 272(3), 598-607 (2013-08-08)
We explored the mechanisms underlying the differential effects of two olfactory toxicants, the herbicide 2,6-dichlorobenzonitrile (DCBN) and the anti-thyroid drug methimazole (MMZ), on olfactory receptor neuron (ORN) regeneration in mouse olfactory epithelium (OE). DCBN, but not MMZ, induced inflammation-like pathological
Guang-Cai Chen et al.
Journal of hazardous materials, 188(1-3), 156-163 (2011-02-18)
The effect of lead on the adsorption of diuron and dichlobenil on multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) was investigated to explore the possible application of MWCNTs for removal of both herbicides from contaminated water. The adsorption of diuron and dichlobenil on
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico