927252
TissueFab® bioink
(GelAlgHA)MA Vis/405 nm, low endotoxin
Sinónimos:
AlgMA, GelMA, HAMA
About This Item
Productos recomendados
descripción
HNMR in D2O at 40°C
Nivel de calidad
Formulario
(viscous liquid to gel)
impurezas
<5 CFU/g Bioburden (Fungal)
<5 CFU/g Bioburden (Total Aerobic)
<50 EU/mL Endotoxin
color
pale yellow to colorless
pH
6.5-7.5
viscosidad
10-30 cP(37 °C)
temp. de almacenamiento
2-8°C
¿Está buscando productos similares? Visita Guía de comparación de productos
Descripción general
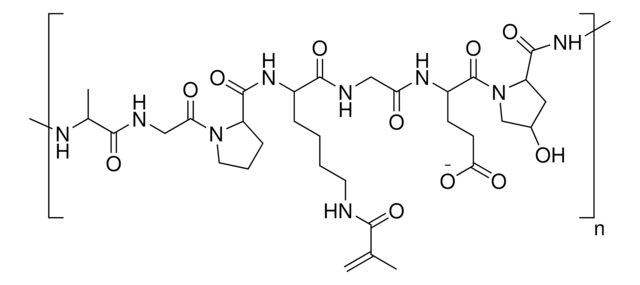
3D bioprinting is the printing of biocompatible materials, cells, growth factors, and the other supporting materials necessary to yield functional complex living tissues. Gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) is a polymerizable hydrogel material derived from natural extracellular matrix (ECM) components. Due to its low cost, abundance, and retention of natural cell binding motifs, gelatin has become a highly sought material for tissue engineering applications. Hyaluronic acid (HA) is a linear polysaccharide of alternating D-glucuronic acid, and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine found in the extracellular matrix. HA is commonly chemically modified to form covalently crosslinked hydrogels. Alginate methacryloyl also known as AlgMA, is a polysaccharide widely used in tissue engineering obtained from brown algae.
Aplicación
Low Endotoxin, low bioburden: Endotoxins have been demonstrated negatively impact cellular growth, morphology, differentiation, inflammation and protein expression. Bioburden is defined as the number of contaminated organisms found in a given amount of material. We test each lot for endotoxins as well as total bioburden (aerobic and fungal) to minimize unwanted interactions. For more information: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/US/en/technical-documents/technical-article/microbiological-testing/pyrogen-testing/what-is-endotoxin
Envase
Información legal
Producto relacionado
Código de clase de almacenamiento
10 - Combustible liquids
Clase de riesgo para el agua (WGK)
WGK 3
Elija entre una de las versiones más recientes:
Certificados de análisis (COA)
It looks like we've run into a problem, but you can still download Certificates of Analysis from our Documentos section.
Si necesita más asistencia, póngase en contacto con Atención al cliente
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico