900889
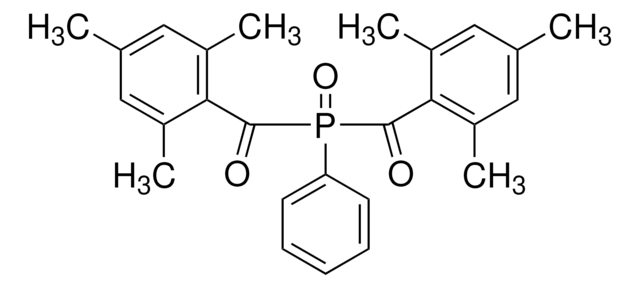
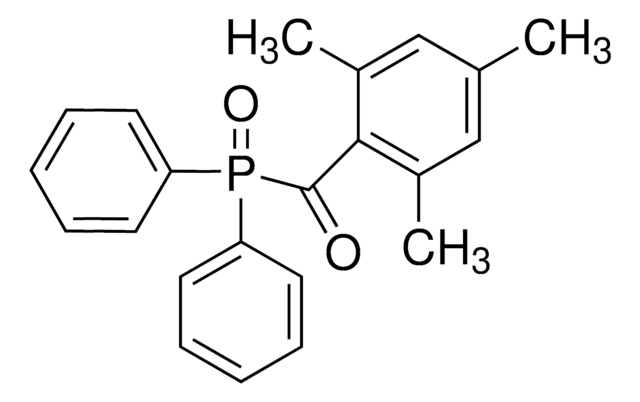
Lithium phenyl-2,4,6-trimethylbenzoylphosphinate
≥95%
Sinónimos:
LAP
About This Item
Productos recomendados
Nivel de calidad
Ensayo
≥95%
Formulario
crystalline powder
color
white to off-white
temp. de almacenamiento
2-8°C
cadena SMILES
CC1=C(C(P(C2=CC=CC=C2)(O[Li])=O)=O)C(C)=CC(C)=C1
¿Está buscando productos similares? Visita Guía de comparación de productos
Categorías relacionadas
Aplicación
Características y beneficios
- Superior water solubility
- Biocompatible
- Sensitiveto visible light
Código de clase de almacenamiento
11 - Combustible Solids
Clase de riesgo para el agua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto de inflamabilidad (°F)
Not applicable
Punto de inflamabilidad (°C)
Not applicable
Elija entre una de las versiones más recientes:
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Los clientes también vieron
Artículos
The introduction of LAP and water-dispersible photoinitiator nanoparticles of TPO, enables the development of novel formulations for 3D bioprinting, tissue engineering applications, and device manufacturing.
Contenido relacionado
Tissue engineering fabricates tissues cultures from scaffolds, living cells, and biologically active molecules by simulating the microenvironment of the body to repair or replace damaged tissue.
Global Trade Item Number
| Número de referencia del producto (SKU) | GTIN |
|---|---|
| 900889-1G | 4061826648209 |
| 900889-5G | 4061833333433 |
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico