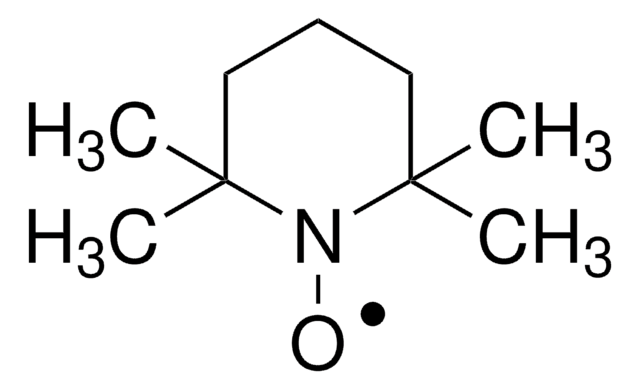
742945
TurboBeads™ TEMPO
≥99%
Sinónimos:
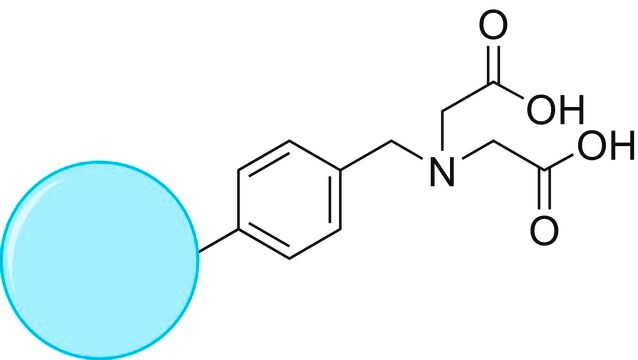
Nano particles, magnetic, TEMPO functionalized
About This Item
Productos recomendados
Línea del producto
TurboBeads™
Análisis
≥99%
formulario
powder
composición
carbon content, ≤14 wt. %
idoneidad de la reacción
reaction type: solution phase peptide synthesis
reactivity: alcohol reactive
Extensión del etiquetado
≥0.1 mmol/g loading (TEMPO)
magnetización
≥120 emu/g, mass saturation
superficie
≥15 m2/g
diámetro promedio
≤50 nm
idoneidad
conforms to structure for Infrared spectrum
Aplicación
Envase
Nota de análisis
air-stability:
weight gain in air at 400°C >20 wt.%
weight gain in air at 100°C <3 wt.%
Información legal
Código de clase de almacenamiento
11 - Combustible Solids
Clase de riesgo para el agua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto de inflamabilidad (°F)
Not applicable
Punto de inflamabilidad (°C)
Not applicable
Elija entre una de las versiones más recientes:
Certificados de análisis (COA)
¿No ve la versión correcta?
Si necesita una versión concreta, puede buscar un certificado específico por el número de lote.
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Artículos
TEMPO (2,2,6,6-Tetramethylpiperidinyloxy or 2,2,6,6-Tetramethylpiperidine 1-oxyl) and its derivatives are stable nitroxy radicals used as catalysts in organic oxidation reactions. TEMPO was discovered by Lebedev and Kazarnovskii in 1960. The stable free radical nature of TEMPO is due to the presence of bulky substituent groups, which hinder the reaction of the free radical with other molecules.
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico