740497
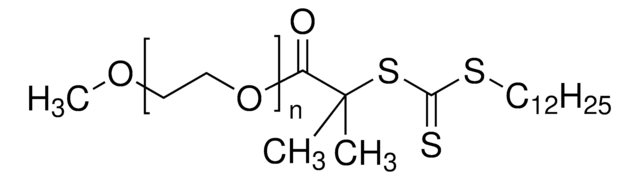
Methyl 2-(dodecylthiocarbonothioylthio)-2-methylpropionate
97% (HPLC)
Sinónimos:
2-[[(Dodecylthio)thioxomethyl]thio]-2-methylpropanoic acid methyl ester
About This Item
Productos recomendados
Nivel de calidad
Análisis
97% (HPLC)
formulario
liquid
índice de refracción
n20/D 1.517
densidad
1.008 g/mL at 25 °C
temp. de almacenamiento
2-8°C
cadena SMILES
CCCCCCCCCCCCSC(=S)SC(C)(C)C(=O)OC
InChI
1S/C18H34O2S3/c1-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15-22-17(21)23-18(2,3)16(19)20-4/h5-15H2,1-4H3
Clave InChI
NHWLEOYMZVCNBC-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Categorías relacionadas
Descripción general
Aplicación
Palabra de señalización
Warning
Frases de peligro
Consejos de prudencia
Clasificaciones de peligro
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Eye Irrit. 2 - Flam. Liq. 3 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Órganos de actuación
Respiratory system
Código de clase de almacenamiento
3 - Flammable liquids
Clase de riesgo para el agua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto de inflamabilidad (°F)
140.0 °F
Punto de inflamabilidad (°C)
60 °C
Elija entre una de las versiones más recientes:
Certificados de análisis (COA)
¿No ve la versión correcta?
Si necesita una versión concreta, puede buscar un certificado específico por el número de lote.
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Los clientes también vieron
Artículos
A series of polymerization were carried out using RAFT agents and monomers yielding well-defined polymers with narrow molecular weight distributions. The process allows radical-initiated growing polymer chains to degeneratively transfer reactivity from one to another through the use of key functional groups (dithioesters, trithiocarbonates, xanthates and dithiocarbamates). RAFT agents help to minimize out-of-control growth and prevent unwanted termination events from occurring, effectively controlling polymer properties like molecular weight and polydispersity. RAFT agents are commercially available. RAFT does not use any cytotoxic heavy metal components (unlike ATRP).
The modification of biomacromolecules, such as peptides and proteins, through the attachment of synthetic polymers has led to a new family of highly advanced biomaterials with enhanced properties.
We presents an article about a micro review of reversible addition/fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization. RAFT (Reversible Addition/Fragmentation Chain Transfer) polymerization is a reversible deactivation radical polymerization (RDRP) and one of the more versatile methods for providing living characteristics to radical polymerization.
Applying ARGET ATRP to the Growth of Polymer Brush Thin Films by Surface-initiated Polymerization
Protocolos
We presents an article featuring procedures that describe polymerization of methyl methacrylate and vinyl acetate homopolymers and a block copolymer as performed by researchers at CSIRO.
Sigma-Aldrich presents an article about RAFT, or Reversible Addition/Fragmentation Chain Transfer, which is a form of living radical polymerization.
Sigma-Aldrich presents an article about the typical procedures for polymerizing via ATRP, which demonstrates that in the following two procedures describe two ATRP polymerization reactions as performed by Prof. Dave Hadddleton′s research group at the University of Warwick.
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
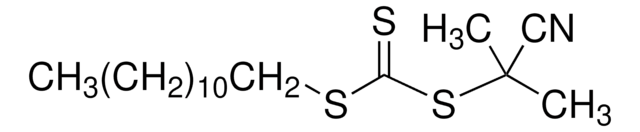
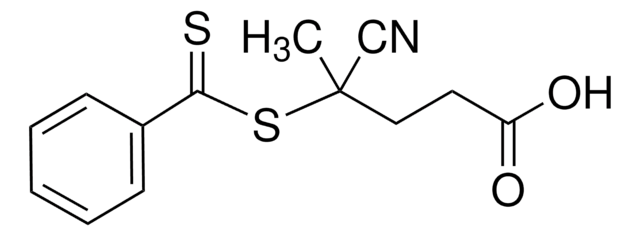
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico![4-Cyano-4-[(dodecylsulfanylthiocarbonyl)sulfanyl]pentanoic acid 97% (HPLC)](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/204/925/30ae6ca0-5b0b-4963-a061-7e5e3d1a85af/640/30ae6ca0-5b0b-4963-a061-7e5e3d1a85af.png)
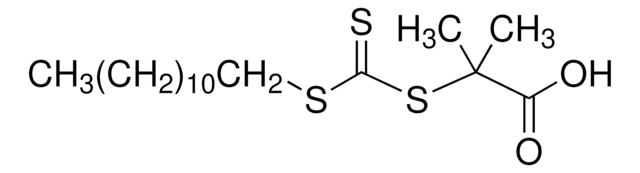
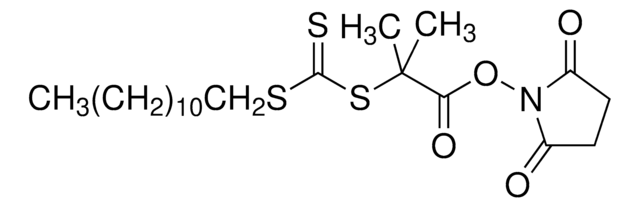
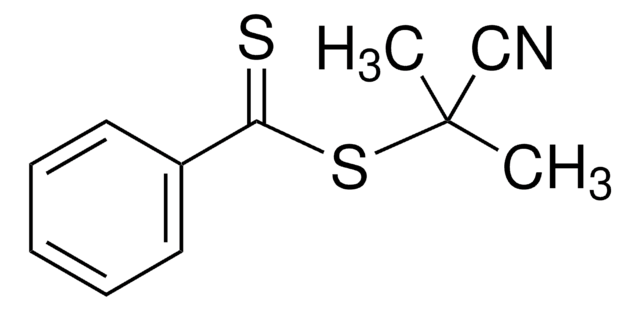
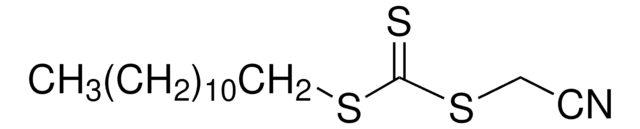
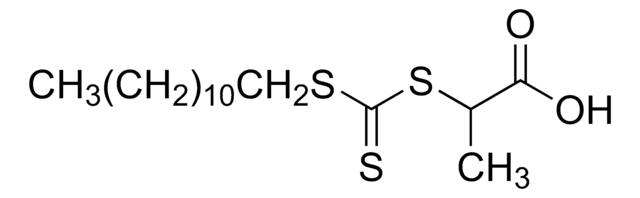
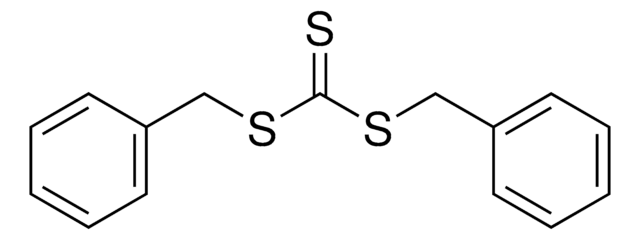
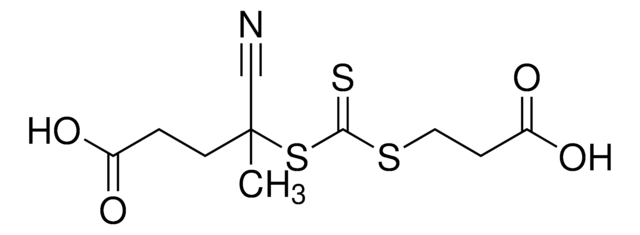


![2-[[(2-Carboxyethyl)sulfanylthiocarbonyl]-sulfanyl]propanoic acid](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/427/606/b02310e2-102e-4324-b09d-e4c0de4fab2c/640/b02310e2-102e-4324-b09d-e4c0de4fab2c.png)
![1,1,1-Tris[(dodecylthiocarbonothioylthio)-2-methylpropionate]ethane 98% (HPLC)](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/233/882/e9f09ad0-62a9-4bbe-b7c0-98b721824fa7/640/e9f09ad0-62a9-4bbe-b7c0-98b721824fa7.png)