475696
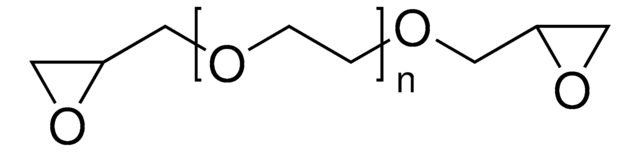
Poly(ethylene glycol) diglycidyl ether
average MN 500, cross-linking reagent amine reactive, glycidyl
Sinónimos:
Polyethylene glycol, Diepoxy PEG, PEG diglycidyl ether, Polyoxyethylene bis(glycidyl ether)
About This Item
Productos recomendados
Nombre del producto
Poly(ethylene glycol) diglycidyl ether, average Mn 500
mol peso
average Mn 500
idoneidad de la reacción
reagent type: cross-linking reagent
reactivity: amine reactive
índice de refracción
n20/D 1.47
Ω-final
epoxy
α-final
epoxy
arquitectura del polímero
shape: linear
functionality: homobifunctional
temp. de almacenamiento
2-8°C
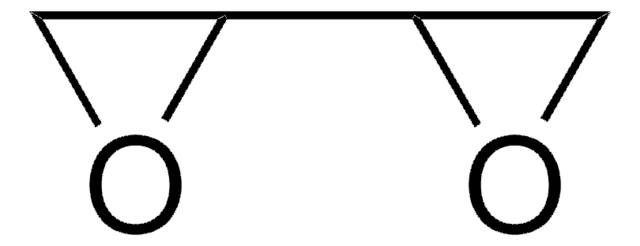
cadena SMILES
O1C(C1)COCCOCC2OC2
InChI
1S/C8H14O4/c1(9-3-7-5-11-7)2-10-4-8-6-12-8/h7-8H,1-6H2
Clave InChI
AOBIOSPNXBMOAT-UHFFFAOYSA-N
¿Está buscando productos similares? Visita Guía de comparación de productos
Categorías relacionadas
Descripción general
Aplicación
Producto relacionado
Código de clase de almacenamiento
10 - Combustible liquids
Clase de riesgo para el agua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto de inflamabilidad (°F)
386.6 °F - closed cup
Punto de inflamabilidad (°C)
197.00 °C - closed cup
Equipo de protección personal
Eyeshields, Gloves
Elija entre una de las versiones más recientes:
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Los clientes también vieron
Artículos
Patterning of PEG-based Hydrogels - Engineering Spatial Complexity
Progress in biotechnology fields such as tissue engineering and drug delivery is accompanied by an increasing demand for diverse functional biomaterials. One class of biomaterials that has been the subject of intense research interest is hydrogels, because they closely mimic the natural environment of cells, both chemically and physically and therefore can be used as support to grow cells. This article specifically discusses poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) hydrogels, which are good for biological applications because they do not generally elicit an immune response. PEGs offer a readily available, easy to modify polymer for widespread use in hydrogel fabrication, including 2D and 3D scaffold for tissue culture. The degradable linkages also enable a variety of applications for release of therapeutic agents.
Devising biomaterial scaffolds that are capable of recapitulating critical aspects of the complex extracellular nature of living tissues in a threedimensional (3D) fashion is a challenging requirement in the field of tissue engineering and regenerative medicine.
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico