456543
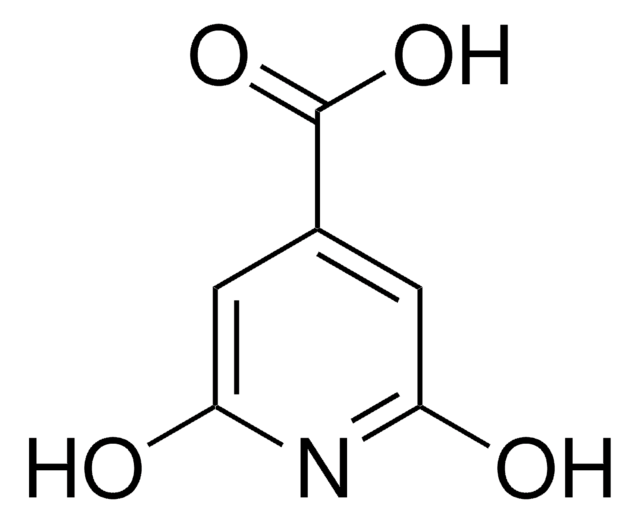
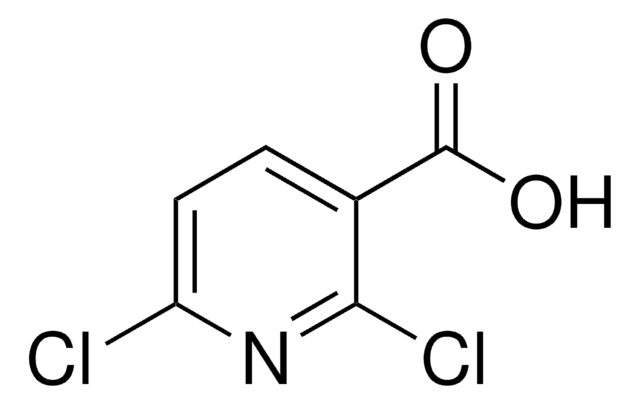
2,6-Dichloropyridine-4-carboxylic acid
98%
Sinónimos:
2,6-Dichloroisonicotinic acid
Iniciar sesiónpara Ver la Fijación de precios por contrato y de la organización
About This Item
Fórmula empírica (notación de Hill):
C6H3Cl2NO2
Número de CAS:
Peso molecular:
192.00
Número MDL:
Código UNSPSC:
12352100
ID de la sustancia en PubChem:
NACRES:
NA.22
Productos recomendados
Nivel de calidad
Ensayo
98%
Formulario
solid
mp
209-212 °C (lit.)
grupo funcional
carboxylic acid
chloro
cadena SMILES
OC(=O)c1cc(Cl)nc(Cl)c1
InChI
1S/C6H3Cl2NO2/c7-4-1-3(6(10)11)2-5(8)9-4/h1-2H,(H,10,11)
Clave InChI
SQSYNRCXIZHKAI-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Categorías relacionadas
Palabra de señalización
Warning
Frases de peligro
Consejos de prudencia
Clasificaciones de peligro
Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Órganos de actuación
Respiratory system
Código de clase de almacenamiento
11 - Combustible Solids
Clase de riesgo para el agua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto de inflamabilidad (°F)
Not applicable
Punto de inflamabilidad (°C)
Not applicable
Equipo de protección personal
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Elija entre una de las versiones más recientes:
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Michael Dalgaard Mikkelsen et al.
Plant physiology, 131(1), 298-308 (2003-01-17)
Glucosinolates are natural plant products that function in the defense toward herbivores and pathogens. Plant defense is regulated by multiple signal transduction pathways in which salicylic acid (SA), jasmonic acid, and ethylene function as signaling molecules. Glucosinolate content was analyzed
The preparation of pyridine-4-carboxylic acid and of piperidine-4-carboxylic acid by catalytic reduction of 2, 6-dichloropyridine-4-carboxylic acid.
Wibaut JP.
Rec. Trav. Chim., 63(7), 141-146 (1944)
J M Manners et al.
Plant molecular biology, 38(6), 1071-1080 (1998-12-30)
The plant defensin PDF1.2 has previously been shown to accumulate systemically via a salicylic acid-independent pathway in leaves of Arabidopsis upon challenge by fungal pathogens. To further investigate the signalling and transcriptional processes underlying plant defensin induction, a DNA fragment
A Guo et al.
The Plant journal : for cell and molecular biology, 15(5), 647-656 (1998-10-21)
A clone encoding a putative soluble epoxide hydrolase (EH-1), an enzyme which converts epoxides to diols, was isolated by differential screening of a cDNA library prepared from tobacco mosaic virus (TMV)-infected tobacco leaves. To confirm that EH-1 encodes an epoxide
European Journal of Organic Chemistry, 22, 4445-4449 (2003)
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico