440248
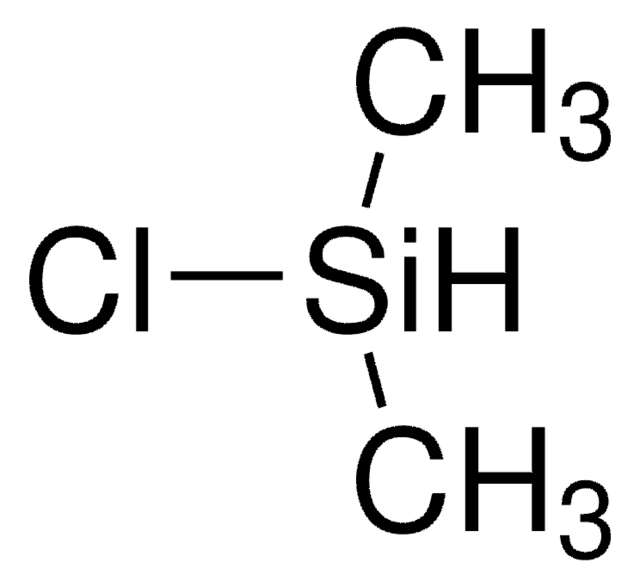
Dichloromethylsilane
≥97%
Sinónimos:
Methyldichlorosilane
About This Item
Productos recomendados
densidad de vapor
4 (vs air)
Nivel de calidad
presión de vapor
6.79 psi ( 20 °C)
Ensayo
≥97%
Formulario
liquid
temp. de autoignición
471 °F
lim. expl.
>55 %
índice de refracción
n20/D 1.398 (lit.)
bp
41 °C (lit.)
mp
−93 °C (lit.)
densidad
1.105 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
temp. de almacenamiento
2-8°C
cadena SMILES
C[SiH](Cl)Cl
InChI
1S/CH4Cl2Si/c1-4(2)3/h4H,1H3
Clave InChI
NWKBSEBOBPHMKL-UHFFFAOYSA-N
¿Está buscando productos similares? Visita Guía de comparación de productos
Categorías relacionadas
Descripción general
Aplicación
- A General and Selective Synthesis of Methylmonochlorosilanes from Di-, Tri-, and Tetrachlorosilanes - Discusses a method for synthesizing Methylmonochlorosilanes, showing potential for varied applications in chemical synthesis (Y Naganawa et al., 2020).
- Polymerization of methylsilylenes into polymethylsilanes or polycarbosilanes after dechlorination of dichloromethylsilanes. - Investigates the polymerization of methylsilylenes, offering insights into the production of polymethylsilanes or polycarbosilanes from Dichloromethylsilanes (Y Tian et al., 2016).
- Synthesis of low viscosity of polymethylhydrosiloxane using monomer of dichloromethylsilane - Focuses on producing low-viscosity polymethylhydrosiloxane through hydrolysis-condensation of Dichloromethylsilane, significant for various industrial applications (VF Arini et al., 2022).
Envase
Palabra de señalización
Danger
Frases de peligro
Clasificaciones de peligro
Acute Tox. 3 Inhalation - Acute Tox. 3 Oral - Eye Dam. 1 - Flam. Liq. 2 - Skin Corr. 1A - Water-react 3
Riesgos supl.
Código de clase de almacenamiento
4.3 - Hazardous materials which set free flammable gases upon contact with water
Clase de riesgo para el agua (WGK)
WGK 1
Punto de inflamabilidad (°F)
-18.4 °F
Punto de inflamabilidad (°C)
-28 °C
Equipo de protección personal
Faceshields, Gloves, Goggles
Elija entre una de las versiones más recientes:
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Los clientes también vieron
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico